Failure to upregulate cell surface PD-1 is associated with dysregulated stimulation of T cells by TGN1412-like CD28 superagonist
- PMID: 25517314
- PMCID: PMC4622985
- DOI: 10.4161/mabs.29758
Failure to upregulate cell surface PD-1 is associated with dysregulated stimulation of T cells by TGN1412-like CD28 superagonist
Abstract
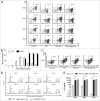
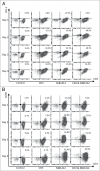
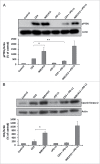
The CD28 superagonist (CD28SA) TGN1412 was administered to humans as an agent that can selectively activate and expand regulatory T cells but resulted in uncontrolled T cell activation accompanied by cytokine storm. The molecular mechanisms that underlie this uncontrolled T cell activation are unclear. Physiological activation of T cells leads to upregulation of not only activation molecules but also inhibitory receptors such as PD-1. We hypothesized that the uncontrolled activation of CD28SA-stimulated T cells is due to both the enhanced expression of activation molecules and the lack of or reduced inhibitory signals. In this study, we show that anti-CD3 antibody-stimulated human T cells undergo time-limited controlled DNA synthesis, proliferation and interleukin-2 secretion, accompanied by PD-1 expression. In contrast, CD28SA-activated T cells demonstrate uncontrolled activation parameters including enhanced expression of LFA-1 and CCR5 but fail to express PD-1 on the cell surface. We demonstrate the functional relevance of the lack of PD-1 mediated regulatory mechanism in CD28SA-stimulated T cells. Our findings provide a molecular explanation for the dysregulated activation of CD28SA-stimulated T cells and also highlight the potential for the use of differential expression of PD-1 as a biomarker of safety for T cell immunostimulatory biologics.
Keywords: APC, antigen presenting cell; CCR5, C-C chemokine receptor type 5; CD28 superagonist; CD28SA, CD28 superagonist; CK2, casein kinase 2; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Antigen 4; IFNγ, interferon gamma; IL-2, interleukin 2; LAG-3, Lymphocyte-activation gene 3; LFA-1, lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; PD-1; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1, programmed cell death-ligand 1; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; S-phase, synthesis phase; T cells; TCR, T cell receptor; TEMs, effector memory T cells; TGN1412; TIM-3, T cell immunoglobulin mucin 3; immunostimulatory biologics.
Figures



References
-
- Pardoll DM. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2012; 12:252-64; PMID:22437870; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrc3239 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gray JC, Johnson PW, Glennie MJ. Therapeutic potential of immunostimulatory monoclonal antibodies. Clin Sci (Lond) 2006; 111:93-106; PMID:16831129; http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/CS20060024 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Suntharalingam G, Perry MR, Ward S, Brett SJ, Castello-Cortes A, Brunner MD, Panoskaltsis N. Cytokine storm in a phase 1 trial of the anti-CD28 monoclonal antibody TGN1412. N Engl J Med 2006; 355:1018-28; PMID:16908486; http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa063842 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stebbings R, Findlay L, Edwards C, Eastwood D, Bird C, North D, Mistry Y, Dilger P, Liefooghe E, Cludts I, et al. . “Cytokine storm” in the phase I trial of monoclonal antibody TGN1412: better understanding the causes to improve preclinical testing of immunotherapeutics. J Immunol 2007; 179:3325-31; PMID:17709549; http://dx.doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.179.5.3325 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Waibler Z, Sender LY, Merten C, Hartig R, Kliche S, Gunzer M, Reichardt P, Kalinke U, Schraven B. Signaling signatures and functional properties of anti-human CD28 superagonistic antibodies. PLoS One 2008; 3:e1708; PMID:18320029; http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001708 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
