Inhibitors of SRC kinases impair antitumor activity of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies
- PMID: 25517315
- PMCID: PMC4622538
- DOI: 10.4161/mabs.32106
Inhibitors of SRC kinases impair antitumor activity of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies
Abstract
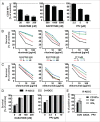
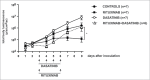
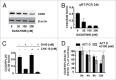
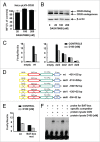
Clinical trials with SRC family kinases (SFKs) inhibitors used alone or in a combination with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are currently underway in the treatment of B-cell tumors. However, molecular interactions between these therapeutics have not been studied so far. A transcriptional profiling of tumor cells incubated with SFKs inhibitors revealed strong downregulation of MS4A1 gene encoding CD20 antigen. In a panel of primary and established B-cell tumors we observed that SFKs inhibitors strongly affect CD20 expression at the transcriptional level, leading to inhibition of anti-CD20 mAbs binding and increased resistance of tumor cells to complement-dependent cytotoxicity. Activation of the AKT signaling pathway significantly protected cells from dasatinib-triggered CD20 downregulation. Additionally, SFKs inhibitors suppressed antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity by direct inhibition of natural killer cells. Abrogation of antitumor activity of rituximab was also observed in vivo in a mouse model. Noteworthy, the effects of SFKs inhibitors on NK cell function are largely reversible. The results of our studies indicate that development of optimal combinations of novel treatment modalities with anti-CD20 mAbs should be preceded by detailed preclinical evaluation of their effects on target cells.
Keywords: ADCC, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; BCR, B-cell receptor; CD20; CDC, complement-dependent cytotoxicity; CFSE, carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; NHL, non-Hodgkin lymphoma; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; SFKs, SRC family kinases; SRC family kinases; dasatinib; ofatumumab; rituximab.
Figures



References
-
- Yamanashi Y, Kakiuchi T, Mizuguchi J, Yamamoto T, Toyoshima K. Association of B cell antigen receptor with protein tyrosine kinase Lyn. Science 1991; 251:192-4; PMID:1702903; http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1702903 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Burkhardt AL, Brunswick M, Bolen JB, Mond JJ. Anti-immunoglobulin stimulation of B lymphocytes activates src-related protein-tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1991; 88:7410-4; PMID:1714601; http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.88.16.7410 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Contri A, Brunati AM, Trentin L, Cabrelle A, Miorin M, Cesaro L, Pinna LA, Zambello R, Semenzato G, Donella-Deana A. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells contain anomalous Lyn tyrosine kinase, a putative contribution to defective apoptosis. J Clin Invest 2005; 115:369-78; PMID:15650771; http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/JCI200522094 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tauzin S, Ding H, Khatib K, Ahmad I, Burdevet D, van Echten-Deckert G, Lindquist JA, Schraven B, Din NU, Borisch B, et al. . Oncogenic association of the Cbp/PAG adaptor protein with the Lyn tyrosine kinase in human B-NHL rafts. Blood 2008; 111:2310-20; PMID:18070987; http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-05-090985 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Packard TA, Cambier JC. B lymphocyte antigen receptor signaling: initiation, amplification, and regulation. F1000Prime Rep 2013; 5:40; PMID:24167721; http://dx.doi.org/10.12703/P5-40 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
