Astrocytes refine cortical connectivity at dendritic spines
- PMID: 25517933
- PMCID: PMC4286724
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.04047
Astrocytes refine cortical connectivity at dendritic spines
Abstract
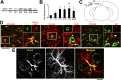
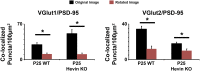
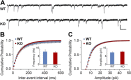
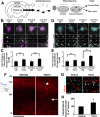
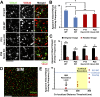
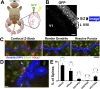
During cortical synaptic development, thalamic axons must establish synaptic connections despite the presence of the more abundant intracortical projections. How thalamocortical synapses are formed and maintained in this competitive environment is unknown. Here, we show that astrocyte-secreted protein hevin is required for normal thalamocortical synaptic connectivity in the mouse cortex. Absence of hevin results in a profound, long-lasting reduction in thalamocortical synapses accompanied by a transient increase in intracortical excitatory connections. Three-dimensional reconstructions of cortical neurons from serial section electron microscopy (ssEM) revealed that, during early postnatal development, dendritic spines often receive multiple excitatory inputs. Immuno-EM and confocal analyses revealed that majority of the spines with multiple excitatory contacts (SMECs) receive simultaneous thalamic and cortical inputs. Proportion of SMECs diminishes as the brain develops, but SMECs remain abundant in Hevin-null mice. These findings reveal that, through secretion of hevin, astrocytes control an important developmental synaptic refinement process at dendritic spines.
Keywords: astrocytes; cell biology; dendritic spines; mouse; neuroscience; synaptogenesis; thalamocortical.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures




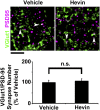
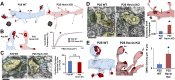
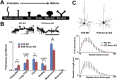


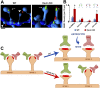
References
-
- De Rubeis S, Pasciuto E, Li KW, Fernandez E, Di Marino D, Buzzi A, Ostroff LE, Klann E, Zwartkruis FJ, Komiyama NH, Grant SG, Poujol C, Choquet D, Achsel T, Posthuma D, Smit AB, Bagni C. CYFIP1 coordinates mRNA translation and cytoskeleton remodeling to ensure proper dendritic spine formation. Neuron. 2013;79:1169–1182. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.06.039. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- De Rubeis S, He X, Goldberg AP, Poultney CS, Samocha K, Cicek AE, Kou Y, Liu L, Fromer M, Walker S, Singh T, Klei L, Kosmicki J, Shih-Chen F, Aleksic B, Biscaldi M, Bolton PF, Brownfeld JM, Cai J, Campbell NG, Carracedo A, Chahrour MH, Chiocchetti AG, Coon H, Crawford EL, Curran SR, Dawson G, Duketis E, Fernandez BA, Gallagher L, Geller E, Guter SJ, Hill RS, Ionita-Laza J, Jimenz Gonzalez P, Kilpinen H, Klauck SM, Kolevzon A, Lee I, Lei I, Lei J, Lehtimäki T, Lin CF, Ma'ayan A, Marshall CR, McInnes AL, Neale B, Owen MJ, Ozaki N, Parellada M, Parr JR, Purcell S, Puura K, Rajagopalan D, Rehnström K, Reichenberg A, Sabo A, Sachse M, Sanders SJ, Schafer C, Schulte-Rüther M, Skuse D, Stevens C, Szatmari P, Tammimies K, Valladares O, Voran A, Li-San W, Weiss LA, Willsey AJ, Yu TW, Yuen RK, DDD Study, Homozygosity Mapping Collaborative for Autism, UK10K Consortium. Cook EH, Freitag CM, Gill M, Hultman CM, Lehner T, Palotie A, Schellenberg GD, Sklar P, State MW, Sutcliffe JS, Walsh CA, Scherer SW, Zwick ME, Barett JC, Cutler DJ, Roeder K, Devlin B, Daly MJ, Buxbaum JD. Synaptic, transcriptional and chromatin genes disrupted in autism. Nature. 2014;515:209–215. doi: 10.1038/nature13772. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS059957/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1F32NS083283/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007184/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS059957/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS071008/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS083897/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS051156/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 2T32NS51156-6/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007171/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS071008/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD040372/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS059957/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD018655/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- MH103374/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- NS083897/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 NS083283/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA031833/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH103374/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

