Antihypertensive potential of the aqueous extract which combine leaf of Persea americana Mill. (Lauraceae), stems and leaf of Cymbopogon citratus (D.C) Stapf. (Poaceae), fruits of Citrus medical L. (Rutaceae) as well as honey in ethanol and sucrose experimental model
- PMID: 25519078
- PMCID: PMC4301628
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-507
Antihypertensive potential of the aqueous extract which combine leaf of Persea americana Mill. (Lauraceae), stems and leaf of Cymbopogon citratus (D.C) Stapf. (Poaceae), fruits of Citrus medical L. (Rutaceae) as well as honey in ethanol and sucrose experimental model
Abstract
Background: The present study was designed to evaluate the effects of the aqueous extract obtained from the mixture of fresh leaf of Persea americana, stems and fresh leaf of Cymbopogon citratus, fruits of Citrus medica and honey on ethanol and sucrose induced hypertension in rats.
Methods: Rats were divided into eight groups of 6 rats each and daily treated for 5 weeks. The control group received distilled water (1 mL/kg) while rats of groups 2, 3 and 4 received ethanol 40 degrees (3 g/kg/day), 10% sucrose as drinking water and the two substances respectively. The remaining groups received in addition to sucrose and ethanol, the aqueous extract (50, 100 and 150 mg/kg) or nifedipine (10 mg/kg) respectively. Many parameters including hemodynamic, biochemical and histopathological were assessed at the end of the study.
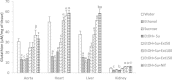
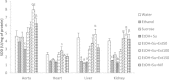
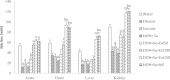
Results: The concomitant consumption of ethanol and sucrose significantly (p < 0.001) increased the blood pressure and the heart rate compared to distilled water treated-rats. The levels of total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, triglycerides, atherogenic index, glucose, proteins, AST, ALT, creatinin, potassium, sodium and albumin increased while the HDL-cholesterol decreased under ethanol and sucrose feeding. Chronic ethanol and sucrose intake significantly decreased the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) as well as the contents of reduced glutathione (GSH) and nitrites whereas elevated the malondialdehyde (MDA) levels. Histological analysis revealed among other vascular congestion, inflammation, tubular clarification and thickening of the vessel wall in rats treated with alcohol and sucrose. Administration of the aqueous extract or nifedipine prevented the hemodynamic, biochemical, oxidative and histological impairments induced chronic ethanol and sucrose consumption.
Conclusion: Current results suggest that the aqueous extract used in this study possess antihypertensive activity against ethanol and sucrose induced hypertension in rats by the improvement of biochemical and oxidative status, and by protecting liver, kidney and vascular endothelium against damages induced by chronic consumption of ethanol and sucrose.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Preventive Potential of the Aqueous Extract of the Mixture of Bidens pilosa (Asteraceae) and Cymbopogon citratus (Poaceae) Aerial Parts on Hypertension Induced by a Chronic Salt and Alcohol Consumption on the Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Mar 9;2022:1980622. doi: 10.1155/2022/1980622. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35310038 Free PMC article.
-
Antihypertensive and antioxidant effects of Allanblackia floribunda Oliv. (Clusiaceae) aqueous extract in alcohol- and sucrose-induced hypertensive rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2010 Apr 21;128(3):634-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.02.025. Epub 2010 Mar 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20193752
-
Antihypertensive and antidiabetic activities of Erythrina senegalensis DC (Fabaceae) stem bark aqueous extract on diabetic hypertensive rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Jan 10;246:112200. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112200. Epub 2019 Aug 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31472272
-
Acute and chronic antihypertensive effects of Cinnamomum zeylanicum stem bark methanol extract in L-NAME-induced hypertensive rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013 Jan 31;13:27. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-13-27. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013. PMID: 23368533 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular effects of Persea americana Mill (Lauraceae) (avocado) aqueous leaf extract in experimental animals.Cardiovasc J Afr. 2007 Mar-Apr;18(2):69-76. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2007. PMID: 17497042
Cited by
-
Avocado (Persea americana) pulp improves cardiovascular and autonomic recovery following submaximal running: a crossover, randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled trial.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 1;10(1):10703. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67577-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32612186 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Citrus Species Against Metabolic Syndrome: Insights from Preclinical and Clinical Studies.Curr Nutr Rep. 2025 Aug 13;14(1):101. doi: 10.1007/s13668-025-00691-8. Curr Nutr Rep. 2025. PMID: 40804580 Review.
-
Preventive Potential of the Aqueous Extract of the Mixture of Bidens pilosa (Asteraceae) and Cymbopogon citratus (Poaceae) Aerial Parts on Hypertension Induced by a Chronic Salt and Alcohol Consumption on the Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Mar 9;2022:1980622. doi: 10.1155/2022/1980622. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35310038 Free PMC article.
-
Acute and Subchronic Toxicity Studies on the Aqueous Extract of the Plant Mixture (Bidens pilosa and Cymbopogon citratus Aerial Parts) in Rat Model.J Toxicol. 2022 Dec 2;2022:1998433. doi: 10.1155/2022/1998433. eCollection 2022. J Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36506716 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Anti-Hypertensive Potential of Lemongrass-A Comprehensive Review.Biology (Basel). 2022 Sep 22;11(10):1382. doi: 10.3390/biology11101382. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290288 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bilanda DC, Dimo T, Djomeni DDP, Bella TMN, Aboubakar OBF, Nguelefack BT, Tan VP, Kamtchouing P. Antihypertensive and antioxidant effects of Allanblackia floribunda Oliv. (Clusiaceae) aqueous in alcohol- and sucrose-induced hypertensive rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010;128:634–640. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.02.025. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aboubakar OBF, Bella NMT, Ngo LTE, Bilanda DC, Dimo T. Antihypertensive activity of Jateorhiza macrantha (Menispermaceae) aqueous extract on ethanol-induced hypertension in wistar. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2012;4:293–298.
-
- Parks EJ, Hellerstein MK. Carbohydrate-induced hypertriacylglycerolemia: historical perspective and review of biological mechanisms. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;71:412–433. - PubMed
-
- Rao SP, Fried S. Sugars, hypertriglyceridesmia, and cardiovascular disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003;78:873–880. - PubMed
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6882/14/507/prepub
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

