Telomerase expression confers cardioprotection in the adult mouse heart after acute myocardial infarction
- PMID: 25519492
- PMCID: PMC4871230
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms6863
Telomerase expression confers cardioprotection in the adult mouse heart after acute myocardial infarction
Abstract
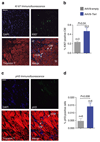
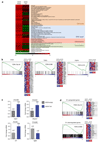
Coronary heart disease is one of the main causes of death in the developed world, and treatment success remains modest, with high mortality rates within 1 year after myocardial infarction (MI). Thus, new therapeutic targets and effective treatments are necessary. Short telomeres are risk factors for age-associated diseases, including heart disease. Here we address the potential of telomerase (Tert) activation in prevention of heart failure after MI in adult mice. We use adeno-associated viruses for cardiac-specific Tert expression. We find that upon MI, hearts expressing Tert show attenuated cardiac dilation, improved ventricular function and smaller infarct scars concomitant with increased mouse survival by 17% compared with controls. Furthermore, Tert treatment results in elongated telomeres, increased numbers of Ki67 and pH3-positive cardiomyocytes and a gene expression switch towards a regeneration signature of neonatal mice. Our work suggests telomerase activation could be a therapeutic strategy to prevent heart failure after MI.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
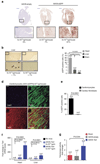
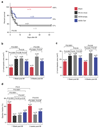
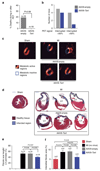
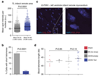

References
-
- Mudd JO, Kass DA. Tackling heart failure in the twenty-first century. Nature. 2008;451:919–928. - PubMed
-
- Liew CC, Dzau VJ. Molecular genetics and genomics of heart failure. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:811–825. - PubMed
-
- Cohn JN, Ferrari R, Sharpe N. Cardiac remodeling--concepts and clinical implications: a consensus paper from an international forum on cardiac remodeling. Behalf of an International Forum on Cardiac Remodeling. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;35:569–582. - PubMed
-
- Dominguez LJ, et al. Ageing, lifestyle modifications, and cardiovascular disease in developing countries. J Nutr Health Aging. 2006;10:143–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

