Coordinated regulation of the orosomucoid-like gene family expression controls de novo ceramide synthesis in mammalian cells
- PMID: 25519910
- PMCID: PMC4317021
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.595116
Coordinated regulation of the orosomucoid-like gene family expression controls de novo ceramide synthesis in mammalian cells
Abstract
The orosomucoid-like (ORMDL) protein family is involved in the regulation of de novo sphingolipid synthesis, calcium homeostasis, and unfolded protein response. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that increase ORMDL3 expression have been associated with various immune/inflammatory diseases, although the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying this association are poorly understood. ORMDL proteins are claimed to be inhibitors of the serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT). However, it is not clear whether individual ORMDL expression levels have an impact on ceramide synthesis. The present study addressed the interaction with and regulation of SPT activity by ORMDLs to clarify their pathophysiological relevance. We have measured ceramide production in HEK293 cells incubated with palmitate as a direct substrate for SPT reaction. Our results showed that a coordinated overexpression of the three isoforms inhibits the enzyme completely, whereas individual ORMDLs are not as effective. Immunoprecipitation and fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) studies showed that mammalian ORMDLs form oligomeric complexes that change conformation depending on cellular sphingolipid levels. Finally, using macrophages as a model, we demonstrate that mammalian cells modify ORMDL genes expression levels coordinately to regulate the de novo ceramide synthesis pathway. In conclusion, we have shown a physiological modulation of SPT activity by general ORMDL expression level regulation. Moreover, because single ORMDL3 protein alteration produces an incomplete inhibition of SPT activity, this work argues against the idea that ORMDL3 pathophysiology could be explained by a simple on/off mechanism on SPT activity.
Keywords: Ceramide; Enzyme Inhibitor; Macrophage; Serine Palmitoyltransferase; Sphingolipid.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
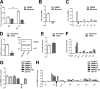
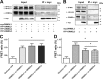
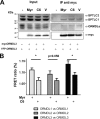
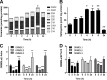
Similar articles
-
The ORMDL/Orm-serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT) complex is directly regulated by ceramide: Reconstitution of SPT regulation in isolated membranes.J Biol Chem. 2019 Mar 29;294(13):5146-5156. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.007291. Epub 2019 Jan 30. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30700557 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9 deletion of ORMDLs reveals complexity in sphingolipid metabolism.J Lipid Res. 2021;62:100082. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2021.100082. Epub 2021 Apr 30. J Lipid Res. 2021. PMID: 33939982 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the ORMDLS, modulators of serine palmitoyltransferase, is regulated by sphingolipids in mammalian cells.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jan 2;290(1):90-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.588236. Epub 2014 Nov 13. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25395622 Free PMC article.
-
Orm/ORMDL proteins: Gate guardians and master regulators.Adv Biol Regul. 2018 Dec;70:3-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2018.08.002. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Adv Biol Regul. 2018. PMID: 30193828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis by the ORMDL proteins and sphingosine kinase-1.Adv Biol Regul. 2015 Jan;57:42-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2014.09.002. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Adv Biol Regul. 2015. PMID: 25319495 Review.
Cited by
-
Aberrant ORM (yeast)-like protein isoform 3 (ORMDL3) expression dysregulates ceramide homeostasis in cells and ceramide exacerbates allergic asthma in mice.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 Oct;136(4):1035-46.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.02.031. Epub 2015 Apr 2. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25842287 Free PMC article.
-
ORMDL proteins regulate ceramide levels during sterile inflammation.J Lipid Res. 2016 Aug;57(8):1412-22. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M065920. Epub 2016 Jun 16. J Lipid Res. 2016. PMID: 27313060 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of serine palmitoyl transferase and ORMDL3 polymorphism are associated with eosinophilic inflammation and airflow limitation in aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 8;15(10):e0240334. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240334. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33031402 Free PMC article.
-
ER Stress and the UPR in Shaping Intestinal Tissue Homeostasis and Immunity.Front Immunol. 2019 Dec 4;10:2825. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02825. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31867005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ceramide Imbalance and Impaired TLR4-Mediated Autophagy in BMDM of an ORMDL3-Overexpressing Mouse Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 20;20(6):1391. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061391. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30897694 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moffatt M. F., Kabesch M., Liang L., Dixon A. L., Strachan D., Heath S., Depner M., von Berg A., Bufe A., Rietschel E., Heinzmann A., Simma B., Frischer T., Willis-Owen S. A., Wong K. C., Illig T., Vogelberg C., Weiland S. K., von Mutius E., Abecasis G. R., Farrall M., Gut I. G., Lathrop G. M., Cookson W. O. (2007) Genetic variants regulating ORMDL3 expression contribute to the risk of childhood asthma. Nature 448, 470–473 - PubMed
-
- McGovern D. P., Gardet A., Törkvist L., Goyette P., Essers J., Taylor K. D., Neale B. M., Ong R. T., Lagacé C., Li C., Green T., Stevens C. R., Beauchamp C., Fleshner P. R., Carlson M., D'Amato M., Halfvarson J., Hibberd M. L., Lördal M., Padyukov L., Andriulli A., Colombo E., Latiano A., Palmieri O., Bernard E. J., Deslandres C., Hommes D. W., de Jong D. J., Stokkers P. C., Weersma R. K., NIDDK IBD Genetics Consortium, Sharma Y., Silverberg M. S., Cho J. H., Wu J., Roeder K., Brant S. R., Schumm L. P., Duerr R. H., Dubinsky M. C., Glazer N. L., Haritunians T., Ippoliti A., Melmed G. Y., Siscovick D. S., Vasiliauskas E. A., Targan S. R., Annese V., Wijmenga C., Pettersson S., Rotter J. I., Xavier R. J., Daly M. J., Rioux J. D., Seielstad M. (2010) Genome-wide association identifies multiple ulcerative colitis susceptibility loci. Nat. Genet. 42, 332–337 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barrett J. C., Hansoul S., Nicolae D. L., Cho J. H., Duerr R. H., Rioux J. D., Brant S. R., Silverberg M. S., Taylor K. D., Barmada M. M., Bitton A., Dassopoulos T., Datta L. W., Green T., Griffiths A. M., Kistner E. O., Murtha M. T., Regueiro M. D., Rotter J. I., Schumm L. P., Steinhart A. H., Targan S. R., Xavier R. J., NIDDK IBD Genetics Consortium, Libioulle C., Sandor C., Lathrop M., Belaiche J., Dewit O., Gut I., Heath S., Laukens D., Mni M., Rutgeerts P., Van Gossum A., Zelenika D., Franchimont D., Hugot J. P., de Vos M., Vermeire S., Louis E., Belgian-French IBD Consortium, Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium, Cardon L. R., Anderson C. A., Drummond H., Nimmo E., Ahmad T., Prescott N. J., Onnie C. M., Fisher S. A., Marchini J., Ghori J., Bumpstead S., Gwilliam R., Tremelling M., Deloukas P., Mansfield J., Jewell D., Satsangi J., Mathew C. G., Parkes M., Georges M., Daly M. J. (2008) Genome-wide association defines more than 30 distinct susceptibility loci for Crohn's disease. Nat. Genet. 40, 955–962 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barrett J. C., Clayton D. G., Concannon P., Akolkar B., Cooper J. D., Erlich H. A., Julier C., Morahan G., Nerup J., Nierras C., Plagnol V., Pociot F., Schuilenburg H., Smyth D. J., Stevens H., Todd J. A., Walker N. M., Rich S. S. (2009) Genome-wide association study and meta-analysis find that over 40 loci affect risk of type 1 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 41, 703–707 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

