Evaluation of national trends in the utilization of partial nephrectomy in relation to the publication of the American Urologic Association guidelines for the management of clinical T1 renal masses
- PMID: 25519922
- PMCID: PMC4289557
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2490-14-101
Evaluation of national trends in the utilization of partial nephrectomy in relation to the publication of the American Urologic Association guidelines for the management of clinical T1 renal masses
Abstract
Background: Partial nephrectomy has been underutilized in the United States. We investigated national trends in partial nephrectomy (PN) utilization before and after publication of the American Urological Association (AUA) Practice Guideline for management of the clinical T1 renal mass.
Methods: We identified adult patients who underwent radical (RN) or PN from November 2007 to October 2011 in the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS). PN prevalence was calculated prior to (11/2007-10/2009) and after Guidelines publication (11/2009-10/2011) and compared the rate of change by linear regression. We also examined the nephrectomy trends in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Statistical analysis included linear regression to determine point-prevalence of PN rates in CKD patients and logistic regression to identify variables associated with PN.
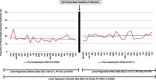
Results: During the study period, 30,944 patients underwent PN and 64,767 RN. The prevalence PN increased from 28.9% in the years prior to guideline release to 35.3% in the years following guideline release with an adjusted odds ratio (OR) of 1.24 (CI 1.01-1.54; p = 0.049). The rate of PN significantly increased throughout the study period (R2 0.15, p = 0.006): however, the rate of change was not increased after the guidelines. (p = 0.46). Overall rate of PN in patients with CKD did not increase over time (R2 0.0007, p = 0.99).
Conclusion: We noted a 6.4% absolute increase in PN after release of the AUA guidelines on clinical T1 renal mass was published; however, the rate of increase was not likely associated with guideline release. The rate of PN performed is increasing; however, further investigation regarding medical decision-making surrounding PN is needed.
Figures

References
-
- Robson CJ, Churchill BM, Anderson W. The results of radical nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 1969;101(3):297–301. - PubMed
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2490/14/101/prepub
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

