Measurement of phenotype and absolute number of circulating heparin-binding hemagglutinin, ESAT-6 and CFP-10, and purified protein derivative antigen-specific CD4 T cells can discriminate active from latent tuberculosis infection
- PMID: 25520147
- PMCID: PMC4308871
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00607-14
Measurement of phenotype and absolute number of circulating heparin-binding hemagglutinin, ESAT-6 and CFP-10, and purified protein derivative antigen-specific CD4 T cells can discriminate active from latent tuberculosis infection
Abstract
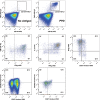
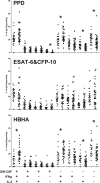
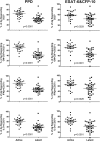
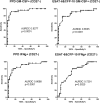
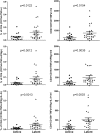
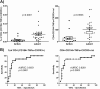
The tuberculin skin test (TST) and interferon gamma (IFN-γ) release assays (IGRAs) are used as adjunctive tests for the evaluation of suspected cases of active tuberculosis (TB). However, a positive test does not differentiate latent from active TB. We investigated whether flow cytometric measurement of novel combinations of intracellular cytokines and surface makers on CD4 T cells could differentiate between active and latent TB after stimulation with Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific proteins. Blood samples from 60 patients referred to the Singapore Tuberculosis Control Unit for evaluation for active TB or as TB contacts were stimulated with purified protein derivative (PPD), ESAT-6 and CFP-10, or heparin-binding hemagglutinin (HBHA). The CD4 T cell cytokine response (IFN-γ, interleukin-2 [IL-2], interleukin-17A [IL-17A], interleukin-22 [IL-22], granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor [GM-CSF], and tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNF-α]) and surface marker expression (CD27, CXCR3, and CD154) were then measured. We found that the proportion of PPD-specific CD4 T cells, defined as CD154(+) TNF-α(+) cells that were negative for CD27 and positive for GM-CSF, gave the strongest discrimination between subjects with latent and those with active TB (area under the receiver operator characteristic [ROC] curve of 0.9277; P < 0.0001). Also, the proportions and absolute numbers of HBHA-specific CD4 T cells were significantly higher in those with latent TB infection, particularly CD154(+) TNF-α(+) IFN-γ(+) IL-2(+) and CD154(+) TNF-α(+) CXCR3(+). Finally, we found that the ratio of ESAT-6- and CFP-10-responding to HBHA-responding CD4 T cells was significantly different between the two study populations. In conclusion, we found novel markers of M. tuberculosis-specific CD4 cells which differentiate between active and latent TB.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Waldrop SL, Pitcher CJ, Peterson DM, Maino VC, Picker LJ. 1997. Determination of antigen-specific memory/effector CD4+ T cell frequencies by flow cytometry: evidence for a novel, antigen-specific homeostatic mechanism in HIV-associated immunodeficiency. J Clin Invest 99:1739–1750. doi: 10.1172/JCI119338. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sester U, Fousse M, Dirks J, Mack U, Prasse A, Singh M, Lalvani A, Sester M. 2011. Whole-blood flow-cytometric analysis of antigen-specific CD4 T-cell cytokine profiles distinguishes active tuberculosis from non-active states. PLoS One 6:e17813. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017813. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harari A, Rozot V, Enders FB, Perreau M, Stalder JM, Nicod LP, Cavassini M, Calandra T, Blanchet CL, Jaton K, Faouzi M, Day CL, Hanekom WA, Bart PA, Pantaleo G. 2011. Dominant TNF-alpha+ Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific CD4+ T cell responses discriminate between latent infection and active disease. Nat Med 17:372–376. doi: 10.1038/nm.2299. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

