Insights into the molecular basis of the NOD2 signalling pathway
- PMID: 25520185
- PMCID: PMC4281710
- DOI: 10.1098/rsob.140178
Insights into the molecular basis of the NOD2 signalling pathway
Abstract
The cytosolic pattern recognition receptor NOD2 is activated by the peptidoglycan fragment muramyl dipeptide to generate a proinflammatory immune response. Downstream effects include the secretion of cytokines such as interleukin 8, the upregulation of pro-interleukin 1β, the induction of autophagy, the production of antimicrobial peptides and defensins, and contributions to the maintenance of the composition of the intestinal microbiota. Polymorphisms in NOD2 are the cause of the inflammatory disorder Blau syndrome and act as susceptibility factors for the inflammatory bowel condition Crohn's disease. The complexity of NOD2 signalling is highlighted by the observation that over 30 cellular proteins interact with NOD2 directly and influence or regulate its functional activity. Previously, the majority of reviews on NOD2 function have focused upon the role of NOD2 in inflammatory disease or in its interaction with and response to microbes. However, the functionality of NOD2 is underpinned by its biochemical interactions. Consequently, in this review, we have taken the opportunity to address the more 'basic' elements of NOD2 signalling. In particular, we have focused upon the core interactions of NOD2 with protein factors that influence and modulate the signal transduction pathways involved in NOD2 signalling. Further, where information exists, such as in relation to the role of RIP2, we have drawn comparison with the closely related, but functionally discrete, pattern recognition receptor NOD1. Overall, we provide a comprehensive resource targeted at understanding the complexities of NOD2 signalling.
Keywords: NLR; NOD1/2; RIP2 kinase; innate immunity; post-translational modification; signal transduction.
Figures

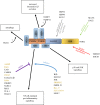

References
-
- Ogura Y, Inohara N, Benito A, Chen FF, Yamaoka S, Nunez G. 2001. Nod2, a Nod1/Apaf-1 family member that is restricted to monocytes and activates NF-κB. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 4812–4818. (doi:10.1074/jbc.M008072200) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bertin J, et al. 1999. Human CARD4 protein is a novel CED-4/Apaf-1 cell death family member that activates NF-κB. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 12 955–12 958. (doi:10.1074/jbc.274.19.12955) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hu Z, et al. 2013. Crystal structure of NLRC4 reveals its autoinhibition mechanism. Science 341, 172–175. (doi:10.1126/science.1236381) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tanabe T, et al. 2004. Regulatory regions and critical residues of NOD2 involved in muramyl dipeptide recognition. EMBO J. 23, 1587–1597. (doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600175) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hampe J, Franke A, Rosenstiel P, Till A. 2007. A genome-wide association scan of nonsynonymous SNPs identifies a susceptibility variant for Crohn disease in ATG16L1. Nat. Genet. 39, 207–211. (doi:10.1038/ng1954) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

