Genotype and risk of major bleeding during warfarin treatment
- PMID: 25521356
- PMCID: PMC4304738
- DOI: 10.2217/pgs.14.153
Genotype and risk of major bleeding during warfarin treatment
Abstract
Aim: To determine whether genetic variants associated with warfarin dose variability were associated with increased risk of major bleeding during warfarin therapy.
Materials & methods: Using Vanderbilt's DNA biobank we compared the prevalence of CYP2C9, VKORC1 and CYP4F2 variants in 250 cases with major bleeding and 259 controls during warfarin therapy.
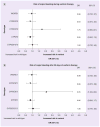
Results: CYP2C9*3 was the only allele that differed significantly among cases (14.2%) and controls (7.8%; p = 0.022). In the 214 (85.6%) cases with a major bleed 30 or more days after warfarin initiation, CYP2C9*3 was the only variant associated with bleeding (adjusted odds ratio: 2.05; 95% CI: 1.04, 4.04).
Conclusion: The CYP2C9*3 allele may double the risk of major bleeding among patients taking warfarin for 30 or more days.
Keywords: CYP2C9; CYP4F2; VKORC1; pharmacogenetics; risk of major bleeding; warfarin.
Figures
References
-
- Keeling D, Baglin T, Tait C, et al. Guidelines on oral anticoagulation with warfarin – fourth edition. Br J Haematol. 2011;154(3):311–324. - PubMed
-
- Kearon C, Ginsberg JS, Kovacs MJ, et al. Comparison of low-intensity warfarin therapy with conventional-intensity warfarin therapy for long-term prevention of recurrent venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(7):631–639. - PubMed
-
- Reynolds MW, Fahrbach K, Hauch O, et al. Warfarin anticoagulation and outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Chest. 2004;126(6):1938–1945. - PubMed
-
- Loebstein R, Yonath H, Peleg D, et al. Interindividual variability in sensitivity to warfarin – nature or nurture? Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2001;70(2):159–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2GM092618/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007569/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 HL065962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004603/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL097036/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- GM109145/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL097036/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 2UL1 TR000445-06/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL056693/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 GM092618/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01HL056693/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM109145/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32GM007569/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U19-HL065962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
