Consensus report of a joint NCI thoracic malignancies steering committee: FDA workshop on strategies for integrating biomarkers into clinical development of new therapies for lung cancer leading to the inception of "master protocols" in lung cancer
- PMID: 25521397
- PMCID: PMC4165474
- DOI: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000314
Consensus report of a joint NCI thoracic malignancies steering committee: FDA workshop on strategies for integrating biomarkers into clinical development of new therapies for lung cancer leading to the inception of "master protocols" in lung cancer
Abstract
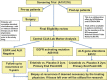
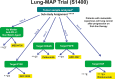
On February 2, 2012, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) sponsored a 2-day workshop with the NCI Thoracic Malignancies Steering Committee and the Food and Drug Administration to bring together leading academicians, clinicians, industry and government representatives to identify challenges and potential solutions in the clinical development of novel targeted therapies for lung cancer. Measures of success are rapidly evolving from a scientific and regulatory perspective and the objectives of this workshop were to achieve initial consensus on a high priority biomarker-driven clinical trial designed to rapidly assess the activity of targeted agents in molecularly defined lung cancer subsets and to facilitate generation of data leading to approval of these new therapies. Additionally, the meeting focused on identification of the barriers to conduct such a trial and the development of strategies to overcome those barriers. The "Lung Master Protocols" recently launched by NCI were the direct outcome of this workshop.
Figures
References
-
- Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2011, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2011/, based on November 2013 SEER data submission. Accessed April. 2014.
-
- Pao W, Hutchinson KE. Chipping away at the lung cancer genome. Nat Med. 2012;18:349–351. - PubMed
-
- Thatcher N, Chang A, Parikh P, et al. Gefitinib plus best supportive care in previously treated patients with refractory advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results from a randomised, placebo-controlled, multicentre study (Iressa Survival Evaluation in Lung Cancer). Lancet. 2005;366:1527–1537. - PubMed
-
- Laleh A-K, Tito F. Why do phase III clinical trials in oncology fail so often? J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012;104:568–569. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

