Immunoglobulins: 25 years of immunoinformatics and IMGT-ONTOLOGY
- PMID: 25521638
- PMCID: PMC4279172
- DOI: 10.3390/biom4041102
Immunoglobulins: 25 years of immunoinformatics and IMGT-ONTOLOGY
Abstract
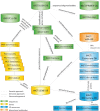
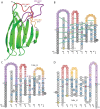
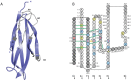
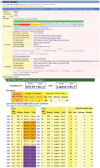
IMGT®, the international ImMunoGeneTics information system® (CNRS and Montpellier University) is the global reference in immunogenetics and immunoinformatics. By its creation in 1989, IMGT® marked the advent of immunoinformatics, which emerged at the interface between immunogenetics and bioinformatics. IMGT® is specialized in the immunoglobulins (IG) or antibodies, T cell receptors (TR), major histocompatibility (MH), and IgSF and MhSF superfamilies. IMGT® has been built on the IMGT-ONTOLOGY axioms and concepts, which bridged the gap between genes, sequences and three-dimensional (3D) structures. The concepts include the IMGT® standardized keywords (identification), IMGT® standardized labels (description), IMGT® standardized nomenclature (classification), IMGT unique numbering and IMGT Colliers de Perles (numerotation). IMGT® comprises seven databases, 15,000 pages of web resources and 17 tools. IMGT® tools and databases provide a high-quality analysis of the IG from fish to humans, for basic, veterinary and medical research, and for antibody engineering and humanization. They include, as examples: IMGT/V-QUEST and IMGT/JunctionAnalysis for nucleotide sequence analysis and their high-throughput version IMGT/HighV-QUEST for next generation sequencing, IMGT/DomainGapAlign for amino acid sequence analysis of IG domains, IMGT/3Dstructure-DB for 3D structures, contact analysis and paratope/epitope interactions of IG/antigen complexes, and the IMGT/mAb-DB interface for therapeutic antibodies and fusion proteins for immunological applications (FPIA).
Figures



References
-
- IMGT®, the international ImMunoGeneTics information system®. [(accessed on 4 November 2014)]. Available online: http://www.imgt.org/
-
- Lefranc M.-P., Lefranc G. The Immunoglobulin FactsBook. Academic Press; London, UK: 2001. pp. 1–458.
-
- Lefranc M.-P., Lefranc G. The T Cell Receptor FactsBook. Academic Press; London, UK: 2001. pp. 1–398.
-
- Lefranc M.-P. Nomenclature of the human immunoglobulin genes. In: Coligan J.E., Bierer B.E., Margulies D.E., Shevach E.M., Strober W., editors. Current Protocols in Immunology. John Wiley and Sons; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2000. pp. 1–37.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

