Assessment of de novo assemblers for draft genomes: a case study with fungal genomes
- PMID: 25521762
- PMCID: PMC4290589
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-S9-S10
Assessment of de novo assemblers for draft genomes: a case study with fungal genomes
Abstract
Background: Recently, large bio-projects dealing with the release of different genomes have transpired. Most of these projects use next-generation sequencing platforms. As a consequence, many de novo assembly tools have evolved to assemble the reads generated by these platforms. Each tool has its own inherent advantages and disadvantages, which make the selection of an appropriate tool a challenging task.
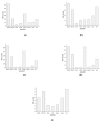
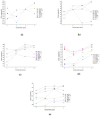
Results: We have evaluated the performance of frequently used de novo assemblers namely ABySS, IDBA-UD, Minia, SOAP, SPAdes, Sparse, and Velvet. These assemblers are assessed based on their output quality during the assembly process conducted over fungal data. We compared the performance of these assemblers by considering both computational as well as quality metrics. By analyzing these performance metrics, the assemblers are ranked and a procedure for choosing the candidate assembler is illustrated.
Conclusions: In this study, we propose an assessment method for the selection of de novo assemblers by considering their computational as well as quality metrics at the draft genome level. We divide the quality metrics into three groups: g1 measures the goodness of the assemblies, g2 measures the problems of the assemblies, and g3 measures the conservation elements in the assemblies. Our results demonstrate that the assemblers ABySS and IDBA-UD exhibit a good performance for the studied data from fungal genomes in terms of running time, memory, and quality. The results suggest that whole genome shotgun sequencing projects should make use of different assemblers by considering their merits.
Figures

References
-
- Wu Y, Gao B, Zhu S. Fungal defensins, an emerging source of anti-infective drugs. Chinese Science Bulletin. 2014;59(10):931–935.
-
- Galagan JE, Henn MR, Ma LJ, Cuomo CA, Birren B. Genomics of the fungal kingdom: insights into eukaryotic biology. Genome Res. 2005;15(12):1620–1631. - PubMed
-
- Birren B, Fink G, Lander E. Fungal genome initiative: a white paper for fungal comparative genomics. Center for Genome Research, Cambridge. 2003.
-
- Luo R, Liu B, Xie Y, Li Z, Huang W, Yuan J, He G, Chen Y, Pan Q, Liu Y, Tang J, Wu G, Zhang H, Shi Y, Liu Y, Yu C, Wang B, Lu Y, Han C, Cheung DW, Yiu SM, Peng S, Xiaoqian Z, Liu G, Liao X, Li Y, Yang H, Wang J, Lam TW, Wang J. SOAPdenovo2: an empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. Giga Science. 2012;1(1):18. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

