Spectral-editing measurements of GABA in the human brain with and without macromolecule suppression
- PMID: 25521836
- PMCID: PMC4470877
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.25549
Spectral-editing measurements of GABA in the human brain with and without macromolecule suppression
Abstract
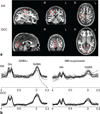
Purpose: The conventional spectral-editing experiment used to measure GABA in the human brain also contains a contribution from macromolecules (MM), and the combined GABA plus MM signal is often referred to as "GABA+". More recently, methods have been developed to estimate GABA free from MM contamination. In this study, the relationship between GABA acquired with MM suppression and conventional GABA+ measurements was examined.
Methods: GABA-edited MEGA-PRESS experiments with and without MM suppression were performed in the sensorimotor and occipital cortex of 12 healthy subjects at 3 Tesla. The correlation between GABA+ and MM-suppressed GABA measures was then determined.
Results: Across all data, a significant correlation between GABA+ and MM-suppressed GABA was found (r = 0.48; P = 0.02). Regionally, the sensorimotor voxel showed a trend toward a correlation of r = 0.53, P = 0.07 and the occipital voxel did not show a correlation, r = 0.058, P = 0.9.
Conclusion: GABA+ and MM-suppressed GABA are moderately correlated, but statistical power to reveal this relationship may vary regionally. The MM signal, while often assumed to be functionally irrelevant, appears to show inter-individual and inter-regional variance that impacts the correlation of GABA+ and MM-suppressed GABA.
Keywords: GABA; brain; edited MRS; macromolecules GABA+.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Sanacora G, Gueorguieva R, Epperson N, Wu Y-T, Appel M, Rothman DL, Krystal JH, Mason GF. Subtype-specific alterations of gaminobutyric acid and glutamate in patients with major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2004;61:705–713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

