Effect of kinase inhibitors on the therapeutic properties of monoclonal antibodies
- PMID: 25523586
- PMCID: PMC4622495
- DOI: 10.4161/19420862.2015.989020
Effect of kinase inhibitors on the therapeutic properties of monoclonal antibodies
Abstract
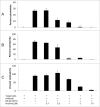
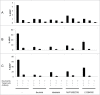
Targeted therapies of malignancies currently consist of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies and small molecule kinase inhibitors. The combination of these novel agents raises the issue of potential antagonisms. We evaluated the potential effect of 4 kinase inhibitors, including the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib, and 3 PI3K inhibitors idelalisib, NVP-BEZ235 and LY294002, on the effects of the 3 monoclonal antibodies, rituximab and obinutuzumab (directed against CD20) and trastuzumab (directed against HER2). We found that ibrutinib potently inhibits antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity exerted by all antibodies, with a 50% inhibitory concentration of 0.2 microM for trastuzumab, 0.5 microM for rituximab and 2 microM for obinutuzumab, suggesting a lesser effect in combination with obinutuzumab than with rituximab. The 4 kinase inhibitors were found to inhibit phagocytosis by fresh human neutrophils, as well as antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis induced by the 3 antibodies. Conversely co-administration of ibrutinib with rituximab, obinutuzumab or trastuzumab did not demonstrate any inhibitory effect of ibrutinib in vivo in murine xenograft models. In conclusion, some kinase inhibitors, in particular, ibrutinib, are likely to exert inhibitory effects on innate immune cells. However, these effects do not compromise the antitumor activity of monoclonal antibodies in vivo in the models that were evaluated.
Keywords: ADCC; ADCC, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; ADCP; ADCP, antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis; NHL, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; NK, natural killer; ibrutinib; idelalisib; kinase inhibitors; monoclonal antibodies; obinutuzumab; rituximab; trastuzumab.
Figures



References
-
- Reichert JM. Antibodies to watch in 2014: Mid-year update. mAbs 2014; 6:799-802; PMID:24846335; http://dx.doi.org/10.4161/mabs.29282 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huang X, Wang S, Lee C-K, Yang X, Liu B. HDAC inhibitor SNDX-275 enhances efficacy of trastuzumab in erbB2-overexpressing breast cancer cells and exhibits potential to overcome trastuzumab resistance. Cancer Lett 2011; 307:72-9; PMID:21497990; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2011.03.019 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gayle SS, Castellino RC, Buss MC, Nahta R. MEK inhibition increases lapatinib sensitivity via modulation of FOXM1. Curr Med Chem 2013; 20:2486-99; PMID:23531216; http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/0929867311320190008 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liang K, Esteva FJ, Albarracin C, Stemke-Hale K, Lu Y, Bianchini G, Yang C-Y, Li Y, Li X, Chen C-T, et al. . Recombinant human erythropoietin antagonizes trastuzumab treatment of breast cancer cells via Jak2-mediated Src activation and PTEN inactivation. Cancer Cell 2010; 18:423-35; PMID:21075308; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2010.10.025 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kohrt HE, Sagiv-Barfi I, Rafiq S, Herman SEM, Butchar JP, Cheney C, Zhang X, Buggy JJ, Muthusamy N, Levy R, et al. . Ibrutinib antagonizes rituximab-dependent NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Blood 2014; 123:1957-60; PMID:24652965; http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-01-547869 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
