Effects of continuous use of Entonox in comparison with intermittent method on obstetric outcomes: a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 25525519
- PMCID: PMC4267458
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/245907
Effects of continuous use of Entonox in comparison with intermittent method on obstetric outcomes: a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Entonox (N2O2) which is an inhalational gas for relieving labor pain is commonly used intermittently; however some women are interested in continuous breathing in face mask. So we decided to compare the complications induced by two methods to find out whether it is safe to permit the mothers to use Entonox continuously or not.
Patients and methods: This randomized clinical trial was performed in Mobini Hospital, Sabzevar, Iran. 50 parturients used Entonox intermittently and 50 cases used it continuously during labor. Then obstetrical outcomes were analyzed in two groups by spss 17 software, t-test, and Chi(2) while P < 0.05 was considered significant.
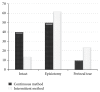
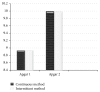
Results: This study showed the mean duration of second stage of labor had no significant difference (P = 0.3). Perineal laceration was less in continuous group significantly (P = 0.04). Assisted vaginal birth was not different significantly (P = 0.4). Uterine atony had no significant difference in two groups (P = 0.2). Maternal collaboration in pushing and satisfaction were higher in continuous group significantly (P = 0.03), (P < 0.0001). Apgar score of neonates at first and fifth minute was acceptable and not different significantly in two groups (P = 0.3).
Conclusions: Our study demonstrated continuous method is also safe. So, it seems reasonable to set mothers free to choose the desired method of Entonox usage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maternal Side-Effects of Continuous vs. Intermittent Method of EntonoxDuring Labor: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Iran J Pharm Res. 2016 Spring;15(2):641-6. Iran J Pharm Res. 2016. PMID: 27642337 Free PMC article.
-
Acceptability of continuous nasal nitrous oxide during labour--a field trial in six maternity hospitals.Anaesthesia. 1981 Apr;36(4):384-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1981.tb10243.x. Anaesthesia. 1981. PMID: 7246989
-
Self-administered Entonox (50% nitrous oxide in oxygen) in labour: report of the experience in Ibadan.Afr J Med Med Sci. 1985 Mar-Jun;14(1-2):95-8. Afr J Med Med Sci. 1985. PMID: 2994447
-
Nitrous Oxide Utility in Labor and Birth: A Multipurpose Modality.J Perinat Neonatal Nurs. 2017 Apr/Jun;31(2):137-144. doi: 10.1097/JPN.0000000000000248. J Perinat Neonatal Nurs. 2017. PMID: 28437304 Review.
-
Labor pain management other than neuraxial: what do we know and where do we go next?Birth. 2012 Dec;39(4):318-22. doi: 10.1111/birt.12009. Epub 2012 Nov 5. Birth. 2012. PMID: 23281953 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the outcomes of normal vaginal delivery with and without spinal anesthesia in mothers admitted to the maternity ward of Firoozabadi Hospital.J Family Med Prim Care. 2022 Sep;11(9):5633-5637. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1998_21. Epub 2022 Oct 14. J Family Med Prim Care. 2022. PMID: 36505630 Free PMC article.
-
Metoclopramide role in preventing ileus after cesarean, a clinical trial.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Jun;71(6):657-662. doi: 10.1007/s00228-015-1845-8. Epub 2015 Apr 15. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25877021 Clinical Trial.
-
A comparison of the effects of ENTONOX inhalation and spinal anesthesia on labor pain reduction and apgar score in vaginal delivery: a clinical trial study.Biomedicine (Taipei). 2018 Sep;8(3):17. doi: 10.1051/bmdcn/2018080317. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Biomedicine (Taipei). 2018. PMID: 30141404 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between COMT Gene Polymorphism, Anxiety, and Pain Perception during Labour.J Clin Med. 2023 Sep 29;12(19):6298. doi: 10.3390/jcm12196298. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37834942 Free PMC article.
-
Childbirth Fear and Associated Factors in a Sample of Pregnant Iranian Women.Oman Med J. 2018 Nov;33(6):497-505. doi: 10.5001/omj.2018.91. Oman Med J. 2018. PMID: 30410692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cunningham F. G., Leveno J. K., Bloom L. S., Hauth C. J., Rouse J. D., Spong Y. C. Williams Obstetrics. 23th. New York, NY, USA: McGraw-Hill; 2010.
-
- Pain relief in childbirth. http://www.entonox.co.uk/en/entonox in medical_therapy with entonox/obst....
-
- Likis F. E., Andrews J. A., Collins M. R., Lewis R. M., Seroogy J. J., Starr S. A., Walden R. R., McPheeters M. L. Comparative Effectiveness Review. 67, AHRQ Publication no. 12-EHC071-EF. Rockville, Md, USA: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; Nitrous oxide for the management of labor pain. http://www.effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov/reports/final.cfm. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources