Effects of continuous use of Entonox in comparison with intermittent method on obstetric outcomes: a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 25525519
- PMCID: PMC4267458
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/245907
Effects of continuous use of Entonox in comparison with intermittent method on obstetric outcomes: a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Entonox (N2O2) which is an inhalational gas for relieving labor pain is commonly used intermittently; however some women are interested in continuous breathing in face mask. So we decided to compare the complications induced by two methods to find out whether it is safe to permit the mothers to use Entonox continuously or not.
Patients and methods: This randomized clinical trial was performed in Mobini Hospital, Sabzevar, Iran. 50 parturients used Entonox intermittently and 50 cases used it continuously during labor. Then obstetrical outcomes were analyzed in two groups by spss 17 software, t-test, and Chi(2) while P < 0.05 was considered significant.
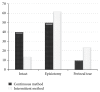
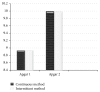
Results: This study showed the mean duration of second stage of labor had no significant difference (P = 0.3). Perineal laceration was less in continuous group significantly (P = 0.04). Assisted vaginal birth was not different significantly (P = 0.4). Uterine atony had no significant difference in two groups (P = 0.2). Maternal collaboration in pushing and satisfaction were higher in continuous group significantly (P = 0.03), (P < 0.0001). Apgar score of neonates at first and fifth minute was acceptable and not different significantly in two groups (P = 0.3).
Conclusions: Our study demonstrated continuous method is also safe. So, it seems reasonable to set mothers free to choose the desired method of Entonox usage.
Figures
References
-
- Cunningham F. G., Leveno J. K., Bloom L. S., Hauth C. J., Rouse J. D., Spong Y. C. Williams Obstetrics. 23th. New York, NY, USA: McGraw-Hill; 2010.
-
- Pain relief in childbirth. http://www.entonox.co.uk/en/entonox in medical_therapy with entonox/obst....
-
- Likis F. E., Andrews J. A., Collins M. R., Lewis R. M., Seroogy J. J., Starr S. A., Walden R. R., McPheeters M. L. Comparative Effectiveness Review. 67, AHRQ Publication no. 12-EHC071-EF. Rockville, Md, USA: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; Nitrous oxide for the management of labor pain. http://www.effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov/reports/final.cfm. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources