A highly conserved program of neuronal microexons is misregulated in autistic brains
- PMID: 25525873
- PMCID: PMC4390143
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.11.035
A highly conserved program of neuronal microexons is misregulated in autistic brains
Abstract
Alternative splicing (AS) generates vast transcriptomic and proteomic complexity. However, which of the myriad of detected AS events provide important biological functions is not well understood. Here, we define the largest program of functionally coordinated, neural-regulated AS described to date in mammals. Relative to all other types of AS within this program, 3-15 nucleotide "microexons" display the most striking evolutionary conservation and switch-like regulation. These microexons modulate the function of interaction domains of proteins involved in neurogenesis. Most neural microexons are regulated by the neuronal-specific splicing factor nSR100/SRRM4, through its binding to adjacent intronic enhancer motifs. Neural microexons are frequently misregulated in the brains of individuals with autism spectrum disorder, and this misregulation is associated with reduced levels of nSR100. The results thus reveal a highly conserved program of dynamic microexon regulation associated with the remodeling of protein-interaction networks during neurogenesis, the misregulation of which is linked to autism.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
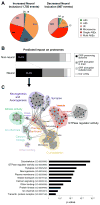
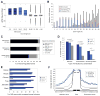
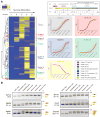

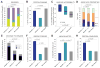


Comment in
-
Microexons--tiny but mighty.EMBO J. 2015 Feb 3;34(3):273-4. doi: 10.15252/embj.201490651. Epub 2014 Dec 22. EMBO J. 2015. PMID: 25535247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barbosa-Morais NL, Irimia M, Pan Q, Xiong HY, Gueroussov S, Lee LJ, Slobodeniuc V, Kutter C, Watt S, Colak R, et al. The evolutionary landscape of alternative splicing in vertebrate species. Science. 2012;338:1587–1593. - PubMed
-
- Barrios-Rodiles M, Brown KR, Ozdamar B, Bose R, Liu Z, Donovan RS, Shinjo F, Liu Y, Dembowy J, Taylor IW, et al. High-throughput mapping of a dynamic signaling network in mammalian cells. Science. 2005;307:1621–1625. - PubMed
-
- Beachy PA, Helfand SL, Hogness DS. Segmental distribution of bithorax complex proteins during Drosophila development. Nature. 1985;313:545–551. - PubMed
-
- Black DL. Does steric interference between splice sites block the splicing of a short c-src neuron-specific exon in non-neuronal cells? Genes Dev. 1991;5:389–402. - PubMed
-
- Borck G, Molla-Herman A, Boddaert N, Encha-Razavi F, Philippe A, Robel L, Desguerre I, Brunelle F, Benmerah A, Munnich A, et al. Clinical, cellular, and neuropathological consequences of AP1S2 mutations: further delineation of a recognizable X-linked mental retardation syndrome. Hum Mutat. 2008;29:966–974. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- BioProject/PRJNA268211
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

