Alectinib salvages CNS relapses in ALK-positive lung cancer patients previously treated with crizotinib and ceritinib
- PMID: 25526238
- PMCID: PMC4304931
- DOI: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000455
Alectinib salvages CNS relapses in ALK-positive lung cancer patients previously treated with crizotinib and ceritinib
Abstract
Background: Leptomeningeal metastases (LM) are an increasingly frequent and devastating complication of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Currently, the optimal management of LM in ALK-positive patients remains poorly understood as these patients have been routinely excluded from clinical trials.
Methods: We describe four ALK-positive patients with LM who were treated with the next-generation ALK inhibitor alectinib through single-patient, compassionate use protocols at two institutions. All patients had previously been treated with both FDA-approved ALK inhibitors--crizotinib and ceritinib. Patients received alectinib at a starting dose of 600 mg twice daily.
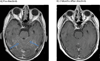
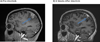
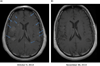
Results: Four ALK-positive NSCLC patients with symptomatic leptomeningeal disease were identified. Three of four patients experienced significant clinical and radiographic improvements in LM upon treatment with alectinib. A fourth patient had stable intracranial disease for 4 months before eventual systemic disease progression. Overall, alectinib was well tolerated. One patient required dose reduction due to grade 2 hyperbilirubinemia.
Conclusions: Alectinib is active in ALK-rearranged NSCLC patients with LM, including in patients previously treated with crizotinib and ceritinib. Additional prospective studies of alectinib in ALK-positive patients with LM are warranted.
Figures
References
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448(7153):561–566. - PubMed
-
- Shaw AT, Kim DW, Nakagawa K, et al. Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(25):2385–2394. - PubMed
-
- Mok T, Kim D, Wu Y, et al. First-line crizotinib versus pemetrexed-cisplatin or pemetrexed-carboplatin in patients (pts) with advanced ALK-positive non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): results of a phase III study (PROFILE 1014) J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:5s. (suppl; abstr 8002)
-
- Kim D-W, Mehra R, Tan DS, et al. Ceritinib in advanced anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-rearranged (ALK+) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Results of the ASCEND-1 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:5S. (suppl; abstr 8003)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

