The coinhibitory receptor CTLA-4 controls B cell responses by modulating T follicular helper, T follicular regulatory, and T regulatory cells
- PMID: 25526313
- PMCID: PMC4309019
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.12.005
The coinhibitory receptor CTLA-4 controls B cell responses by modulating T follicular helper, T follicular regulatory, and T regulatory cells
Abstract
The receptor CTLA-4 has been implicated in controlling B cell responses, but the mechanisms by which CTLA-4 regulates antibody production are not known. Here we showed deletion of CTLA-4 in adult mice increased Tfh and Tfr cell numbers and augmented B cell responses. In the effector phase, loss of CTLA-4 on Tfh cells resulted in heightened B cell responses, whereas loss of CTLA-4 on Tfr cells resulted in defective suppression of antigen-specific antibody responses. We also found that non-Tfr Treg cells could suppress B cell responses through CTLA-4 and that Treg and/or Tfr cells might downregulate B7-2 on B cells outside germinal centers as a means of suppression. Within the germinal center, however, Tfr cells potently suppress B cells through CTLA-4, but with a mechanism independent of altering B7-1 or B7-2. Thus, we identify multifaceted regulatory roles for CTLA-4 in Tfh, Tfr, and Treg cells, which together control humoral immunity.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

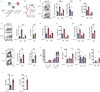
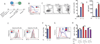
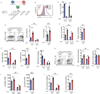

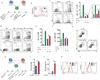

Comment in
-
Treg cells and CTLA-4: the ball and chain of the germinal center response.Immunity. 2014 Dec 18;41(6):876-8. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.12.009. Immunity. 2014. PMID: 25526300
References
-
- Akiba H, Takeda K, Kojima Y, Usui Y, Harada N, Yamazaki T, Ma J, Tezuka K, Yagita H, Okumura K. The role of ICOS in the CXCR5+ follicular B helper T cell maintenance in vivo. J Immunol. 2005;175:2340–2348. - PubMed
-
- Bour-Jordan H, Grogan JL, Tang Q, Auger JA, Locksley RM, Bluestone JA. CTLA-4 regulates the requirement for cytokine-induced signals in T(H)2 lineage commitment. Nature immunology. 2003;4:182–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

