Recent developments in β-cell differentiation of pluripotent stem cells induced by small and large molecules
- PMID: 25526563
- PMCID: PMC4284775
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms151223418
Recent developments in β-cell differentiation of pluripotent stem cells induced by small and large molecules
Abstract
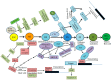
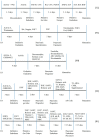
Human pluripotent stem cells, including human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) and human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs), hold promise as novel therapeutic tools for diabetes treatment because of their self-renewal capacity and ability to differentiate into beta (β)-cells. Small and large molecules play important roles in each stage of β-cell differentiation from both hESCs and hiPSCs. The small and large molecules that are described in this review have significantly advanced efforts to cure diabetic disease. Lately, effective protocols have been implemented to induce hESCs and human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) to differentiate into functional β-cells. Several small molecules, proteins, and growth factors promote pancreatic differentiation from hESCs and hMSCs. These small molecules (e.g., cyclopamine, wortmannin, retinoic acid, and sodium butyrate) and large molecules (e.g. activin A, betacellulin, bone morphogentic protein (BMP4), epidermal growth factor (EGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF), keratinocyte growth factor (KGF), hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), noggin, transforming growth factor (TGF-α), and WNT3A) are thought to contribute from the initial stages of definitive endoderm formation to the final stages of maturation of functional endocrine cells. We discuss the importance of such small and large molecules in uniquely optimized protocols of β-cell differentiation from stem cells. A global understanding of various small and large molecules and their functions will help to establish an efficient protocol for β-cell differentiation.
Figures

References
-
- Grundy S.M., Brewer H.B., Cleeman J.I., Smith S.C., Lenfant C. Definition of metabolic syndrome—Report of the national heart, lung, and blood institute/american heart association conference on scientific issues related to definition. Circulation. 2004;109:433–438. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000111245.75752.C6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993;329:997–986. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

