Immunohistochemical determination of the miR-1290 target arylamine N-acetyltransferase 1 (NAT1) as a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer
- PMID: 25528056
- PMCID: PMC4364092
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-990
Immunohistochemical determination of the miR-1290 target arylamine N-acetyltransferase 1 (NAT1) as a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer
Abstract
Background: There are many molecular differences between estrogen receptor α (ERα)-positive and ER-negative breast cancers. Recent analyses have shown that the former can be divided into two subtypes, luminal A and luminal B. These differ in response to endocrine therapy and chemotherapy, and in prognosis. In a previous study, we found that microRNA (miR)-1290 that was significantly down-regulated in luminal A tumors and its potential target arylamine N-acetyltransferase 1 (NAT1). The aim of the present study was to determine whether NAT1 is a bona fide target of miR-1290, and to investigate the impact of NAT1 on breast cancer prognosis.
Methods: Luciferase reporter assays were employed to validate NAT1 as a putative miR-1290 target gene. Expression of NAT1, ERα, progesterone receptor (PgR) and HER2 was analyzed in 394 breast cancer samples by immunohistochemistry.
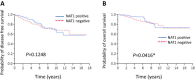
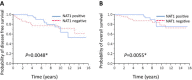
Results: NAT1 was confirmed to be a direct target of miR-1290. Levels of expression of NAT1 were positively correlated with those of ERα (P < 0.0001) and PgR (P < 0.0001), but negatively correlated with both tumor grade and size (P < 0.0001). Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that the presence of NAT1 was significantly associated with increased overall survival (OS) (P = 0.0416) in these patients. Similarly, significant associations of NAT1 with disease-free survival (DFS) (P = 0.0048) and OS (P = 0.0055) in those patients who received adjuvant endocrine therapy with tamoxifen (n = 176) were found. Moreover, NAT1 was also significantly associated with increased DFS (P = 0.0025) and OS (P = 0.0007) in the subset of lymph node-positive patients (n = 147). Univariate and multivariate analyses showed significant associations between levels of NAT1 and DFS (P = 0.0005 and 0.019, respectively).
Conclusions: We report that miR-1290 directly targets the NAT1 3'-UTR and that NAT1 protein expression is correlated with improved OS of breast cancer patients. NAT1 is a possible prognostic biomarker for lymph node-positive breast cancer. Thus, miR-1290 and its target NAT1 are associated with important characteristics of breast cancer.
Figures


Similar articles
-
miR-1290 and its potential targets are associated with characteristics of estrogen receptor α-positive breast cancer.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2013 Feb 18;20(1):91-102. doi: 10.1530/ERC-12-0207. Print 2013 Feb. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23183268
-
Trimodal distribution of arylamine N-acetyltransferase 1 mRNA in breast cancer tumors: association with overall survival and drug resistance.BMC Genomics. 2018 Jul 3;19(1):513. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4894-4. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29969986 Free PMC article.
-
Arylamine N-acetyltransferase 1 expression in breast cancer cell lines: a potential marker in estrogen receptor-positive tumors.Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2008 Feb;47(2):118-26. doi: 10.1002/gcc.20512. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2008. PMID: 17973251
-
Human arylamine N-acetyltransferase 1: a drug-metabolizing enzyme and a drug target?Curr Drug Targets. 2010 Jun;11(6):759-66. doi: 10.2174/138945010791170905. Curr Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20041842 Review.
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of microRNA-21 overexpression in breast cancer: a meta-analysis.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Aug 15;7(9):5622-33. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25337203 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A novel gene expression signature for bone metastasis in breast carcinomas.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Apr;156(2):249-59. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-3741-z. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 26965286 Free PMC article.
-
Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD) regulates autophagy through promoting the expression of Ras homolog enriched in brain (Rheb) in human breast adenocarcinoma cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 26;7(17):24572-84. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8249. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27013580 Free PMC article.
-
The footprint of the ageing stroma in older patients with breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2017 Jul 3;19(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s13058-017-0871-0. Breast Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28673354 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Arylamine N-acetyltransferase 1 and miR-1290 Levels in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Pilot Study.In Vivo. 2023 May-Jun;37(3):1129-1144. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13188. In Vivo. 2023. PMID: 37103073 Free PMC article.
-
A novel gene signature associated with anoikis predicts prognosis and unveils immune infiltration in breast cancer patients.Discov Oncol. 2025 Apr 2;16(1):447. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02213-y. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40172726 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA, Fluge O, Pergamenschikov A, Williams C, Zhu SX, Lonning PE, Borresen-Dale AL, Brown PO, Botstein D. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406(6797):747–752. doi: 10.1038/35021093. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sorlie T, Tibshirani R, Parker J, Hastie T, Marron JS, Nobel A, Deng S, Johnsen H, Pesich R, Geisler S, Demeter J, Perou CM, Lonning PE, Brown PO, Borresen-Dale AL, Botstein D. Repeated observation of breast tumor subtypes in independent gene expression data sets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(14):8418–8423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0932692100. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blenkiron C, Goldstein LD, Thorne NP, Spiteri I, Chin SF, Dunning MJ, Barbosa-Morais NL, Teschendorff AE, Green AR, Ellis IO, Tavare S, Caldas C, Miska EA. MicroRNA expression profiling of human breast cancer identifies new markers of tumor subtype. Genome Biol. 2007;8(10):R214. doi: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-10-r214. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Krol J, Loedige I, Filipowicz W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11(9):597–610. - PubMed
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2407/14/990/prepub
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

