Optogenetic control of intracellular signaling pathways
- PMID: 25529484
- PMCID: PMC4308517
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2014.11.007
Optogenetic control of intracellular signaling pathways
Abstract
Cells employ a plethora of signaling pathways to make their life-and-death decisions. Extensive genetic, biochemical, and physiological studies have led to the accumulation of knowledge about signaling components and their interactions within signaling networks. These conventional approaches, although useful, lack the ability to control the spatial and temporal aspects of signaling processes. The recently emerged optogenetic tools open exciting opportunities by enabling signaling regulation with superior temporal and spatial resolution, easy delivery, rapid reversibility, fewer off-target side effects, and the ability to dissect complex signaling networks. Here we review recent achievements in using light to control intracellular signaling pathways and discuss future prospects for the field, including integration of new genetic approaches into optogenetics.
Keywords: Dronpa; LOV; UVR8; cryptochrome; intracellular signaling pathways; light-induced protein–protein interaction; oligomerization; optogenetics; photoactivatable proteins; phytochrome; signal transduction.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

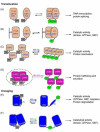
References
-
- Santos SD, Verveer PJ, Bastiaens PI. Growth factor-induced MAPK network topology shapes Erk response determining PC-12 cell fate. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:324–330. - PubMed
-
- Airan RD, Thompson KR, Fenno LE, Bernstein H, Deisseroth K. Temporally precise in vivo control of intracellular signalling. Nature. 2009;458:1025–1029. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

