Lipid-induced NOX2 activation inhibits autophagic flux by impairing lysosomal enzyme activity
- PMID: 25529920
- PMCID: PMC4340303
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M055152
Lipid-induced NOX2 activation inhibits autophagic flux by impairing lysosomal enzyme activity
Abstract
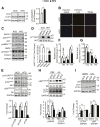
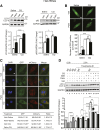
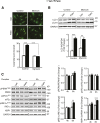
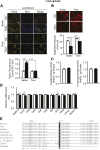
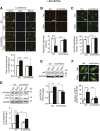
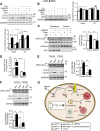
Autophagy is a catabolic process involved in maintaining energy and organelle homeostasis. The relationship between obesity and the regulation of autophagy is cell type specific. Despite adverse consequences of obesity on cardiac structure and function, the contribution of altered cardiac autophagy in response to fatty acid overload is incompletely understood. Here, we report the suppression of autophagosome clearance and the activation of NADPH oxidase (Nox)2 in both high fat-fed murine hearts and palmitate-treated H9C2 cardiomyocytes (CMs). Defective autophagosome clearance is secondary to superoxide-dependent impairment of lysosomal acidification and enzyme activity in palmitate-treated CMs. Inhibition of Nox2 prevented superoxide overproduction, restored lysosome acidification and enzyme activity, and reduced autophagosome accumulation in palmitate-treated CMs. Palmitate-induced Nox2 activation was dependent on the activation of classical protein kinase Cs (PKCs), specifically PKCβII. These findings reveal a novel mechanism linking lipotoxicity with a PKCβ-Nox2-mediated impairment in pH-dependent lysosomal enzyme activity that diminishes autophagic turnover in CMs.
Keywords: NADPH oxidase 2; autophagy; cardiomyocytes; fatty acids; lysosomes; protein kinase Cβ.
Copyright © 2015 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


Comment in
-
A new pathway regulating autophagy.J Lipid Res. 2015 Mar;56(3):485-486. doi: 10.1194/jlr.C057190. Epub 2014 Dec 31. J Lipid Res. 2015. PMID: 25552477 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hubert H. B., Feinleib M., McNamara P. M., Castelli W. P. 1983. Obesity as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease: a 26-year follow-up of participants in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 67: 968–977. - PubMed
-
- Chiu H. C., Kovacs A., Blanton R. M., Han X., Courtois M., Weinheimer C. J., Yamada K. A., Brunet S., Xu H., Nerbonne J. M., et al. 2005. Transgenic expression of fatty acid transport protein 1 in the heart causes lipotoxic cardiomyopathy. Circ. Res. 96: 225–233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

