Homotypic receptor-receptor interactions regulating Eph signaling
- PMID: 25530219
- PMCID: PMC4594565
- DOI: 10.4161/19336918.2014.971684
Homotypic receptor-receptor interactions regulating Eph signaling
Abstract
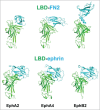
The Eph receptor tyrosine kinases and their ephrin ligands direct axon pathfinding and neuronal cell migration, and mediate many other cell-cell communication events. The Ephs and ephrins both localize to the plasma membrane and, upon cell-cell contact, form extensive signaling assemblies at the contact sites. Recent structural, biochemical and cell-biological studies revealed that these assemblies are generated not only via Eph-ephrin interactions, but also via homotypic interactions between neighboring receptor molecules. In addition, Eph-Eph interactions mediate receptor pre-clustering, which ensures fast and efficient activation once ligands come into contact range. Here we summarize the current knowledge about the homotypic Eph-Eph interactions and discuss how they could modulate the initiation of Eph/ephrin signaling.
Keywords: Eph receptors; cell-cell signaling; ephrins; receptor tyrosine kinases.
Figures


References
-
- Flanagan JG, Vanderhaeghen P. The ephrins and Eph receptors in neural development. Annu Rev Neurosci 1998; 21:309-45; PMID:9530499; http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.21.1.309 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Frisen J, Holmberg J, Barbacid M. Ephrins and their Eph receptors: multitalented directors of embryonic development. EMBO J 1999; 18:5159-65; PMID:10508149; http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/emboj/18.19.5159 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kullander K, Klein R. Mechanisms and functions of EPH and ephrin signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio 2002; 3:475-86; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrm856 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wilkinson DG. Multiple roles of EPH receptors and ephrins in neural development. Nat Rev Neurosci 2001; 2:155-64; PMID:11256076; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35058515 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Holland SJ, Gale NW, Mbamalu G, Yancopoulos GD, Henkemeyer M, Pawson T. Bidirectional signalling through the EPH-family receptor Nuk and its transmembrane ligands. Nature 1996; 383:722-5; PMID:8878483; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/383722a0 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
