Comparison of electroacupuncture and morphine-mediated analgesic patterns in a plantar incision-induced pain model
- PMID: 25530786
- PMCID: PMC4233674
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/659343
Comparison of electroacupuncture and morphine-mediated analgesic patterns in a plantar incision-induced pain model
Abstract
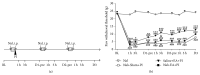
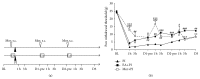
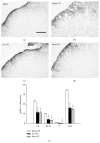
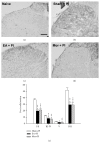
Electroacupuncture (EA) is a complementary therapy to improve morphine analgesia for postoperative pain, but underlying mechanism is not well-known. Herein, we investigated EA-induced analgesic effect in a plantar incision (PI) model in male Sprague-Dawley rats. PI was performed at the left hind paw. EA of 4 Hz and high intensity or sham needling was conducted at right ST36 prior to PI and repeated for another 2 days. Behavioral responses to mechanical and thermal stimuli, spinal phospho-ERK, and Fos expression were all analyzed. In additional groups, naloxone and morphine were administered to elucidate involvement of opioid receptors and for comparison with EA. EA pretreatment significantly reduced post-PI tactile allodynia for over 1 day; repeated treatments maintained analgesic effect. Intraperitoneal naloxone could reverse EA analgesia. Low-dose subcutaneous morphine (1 mg/kg) had stronger inhibitory effect on PI-induced allodynia than EA for 1 h. However, analgesic tolerance appeared after repeated morphine injections. Both EA and morphine could equally inhibit PI-induced p-ERK and Fos inductions. We conclude that though EA and morphine attenuate postincision pain through opioid receptor activations, daily EA treatments result in analgesic accumulation whereas daily morphine injections develop analgesic tolerance. Discrepant pathways and mechanisms underlying two analgesic means may account for the results.
Figures

References
-
- Buvanendran A., Kroin J. S., Tuman K. J., et al. Effects of perioperative administration of a selective cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor on pain management and recovery of function after knee replacement: a randomized controlled trial. The Journal of the American Medical Association. 2003;290(18):2411–2418. doi: 10.1001/jama.290.18.2411. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Remérand F., Le Tendre C., Baud A., Couvret C., Pourrat X., Favard L., Laffon M., Fusciardi J. The early and delayed analgesic effects of ketamine after total hip arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, controlled, double-blind study. Anesthesia and Analgesia. 2009;109(6):1963–1971. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181bdc8a0. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

