Circulating levels of irisin in middle-aged first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetes mellitus - correlation with pancreatic β-cell function
- PMID: 25530809
- PMCID: PMC4271516
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-5996-6-133
Circulating levels of irisin in middle-aged first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetes mellitus - correlation with pancreatic β-cell function
Abstract
Background: Irisin is a novel myokine secreted in response to peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) activation through exercise. The first-degree relatives (FDRs) of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients bear a lifetime risk for developing T2DM, especially after 40 years old. However, the circulating irisin levels in middle-aged FDRs of T2DM is unclear. We therefore investigated the association between circulating irisin and pancreatic β-cell function in normal-glucose-tolerance (NGT) subjects.
Methods: In this cross-sectional study, we recruited 412 supposed healthy subjects aged 40-60 who were FDRs of T2DM patients but without previous diagnosis of T2DM. Of the 412 individuals, 254 had NGT and 60 were newly diagnosed T2DM based on the results of a 75 g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT- World Health Organization diagnostic criteria). We measured irisin in the newly diagnosed T2DM group (n = 60) and in an age- and sex-matched NGT subgroups (n = 62). Serum irisin was quantified by ELISA, and its association with metabolic parameters was analysed by Pearson's correlation and multiple linear regression analyses.
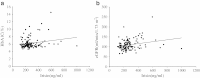
Results: There was no significant difference in serum irisin between middle-aged newly diagnosed T2DM patients and the NGT control group. Circulating irisin was correlated with haemoglobin A1c (r = 0.202, p = 0.026) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (r = 0.239, p = 0.010). Multiple linear regression revealed that only homeostasis model assessment-β (HOMA-β) was associated with irisin in NGT subjects after adjusting for confounding factors. However, similar analysis in T2DM did not reveal a significant association between circulating irisin and metabolic parameters.
Conclusions: There was no significant difference in serum irisin between middle-aged newly diagnosed T2DM patients and the NGT controls. Serum irisin level was closely related to HOMA-β in NGT, suggesting that irisin may play a crucial role in pancreatic β-cell function.
Keywords: First-degree relatives; Irisin; Pancreatic β-cell; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures
References
-
- Voight BF, Scott LJ, Steinthorsdottir V, Morris AP, Dina C, Welch RP, Zeggini E, Huth C, Aulchenko YS, Thorleifsson G, McCulloch LJ, Ferreira T, Grallert H, Amin N, Wu G, Willer CJ, Raychaudhuri S, McCarroll SA, Langenberg C, Hofmann OM, Dupuis J, Qi L, Segrè AV, van Hoek M, Navarro P, Ardlie K, Balkau B, Benediktsson R, Bennett AJ, Blagieva R, et al. Twelve type 2 diabetes susceptibility loci identified through large-scale association analysis. Nat Genet. 2010;42:579–589. doi: 10.1038/ng.609. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alibegovic AC, Højbjerre L, Sonne MP, van Hall G, Stallknecht B, Dela F, Vaag A. Impact of 9 days of bed rest on hepatic and peripheral insulin action, insulin secretion, and whole-body lipolysis in healthy young male offspring of patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2009;58:2749–2756. doi: 10.2337/db09-0369. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources