Use of a Wireless Network of Accelerometers for Improved Measurement of Human Energy Expenditure
- PMID: 25530874
- PMCID: PMC4269939
- DOI: 10.3390/electronics3020205
Use of a Wireless Network of Accelerometers for Improved Measurement of Human Energy Expenditure
Abstract
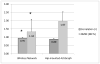
Single, hip-mounted accelerometers can provide accurate measurements of energy expenditure (EE) in some settings, but are unable to accurately estimate the energy cost of many non-ambulatory activities. A multi-sensor network may be able to overcome the limitations of a single accelerometer. Thus, the purpose of our study was to compare the abilities of a wireless network of accelerometers and a hip-mounted accelerometer for the prediction of EE. Thirty adult participants engaged in 14 different sedentary, ambulatory, lifestyle and exercise activities for five minutes each while wearing a portable metabolic analyzer, a hip-mounted accelerometer (AG) and a wireless network of three accelerometers (WN) worn on the right wrist, thigh and ankle. Artificial neural networks (ANNs) were created separately for the AG and WN for the EE prediction. Pearson correlations (r) and the root mean square error (RMSE) were calculated to compare criterion-measured EE to predicted EE from the ANNs. Overall, correlations were higher (r = 0.95 vs. r = 0.88, p < 0.0001) and RMSE was lower (1.34 vs. 1.97 metabolic equivalents (METs), p < 0.0001) for the WN than the AG. In conclusion, the WN outperformed the AG for measuring EE, providing evidence that the WN can provide highly accurate estimates of EE in adults participating in a wide range of activities.
Keywords: ActiGraph; activity measurement; artificial neural network; machine learning; multi-sensor network; physical activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ward DS, Evenson KR, Vaughn A, Rodgers AB, Troiano RP. Accelerometer use in physical activity: Best practices and research recommendations. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2005;37:S582–S588. - PubMed
-
- Freedson PS, Miller K. Objective monitoring of physical activity using motion sensors and heart rate. Res Q Exerc Sport. 2000;71:S21–S29. - PubMed
-
- Freedson PS, Melanson E, Sirard J. Calibration of the Computer Science and Applications, Inc. accelerometer. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1998;30:777–781. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
