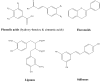
Resources and biological activities of natural polyphenols
- PMID: 25533011
- PMCID: PMC4277013
- DOI: 10.3390/nu6126020
Resources and biological activities of natural polyphenols
Abstract
The oxidative stress imposed by reactive oxygen species (ROS) plays an important role in many chronic and degenerative diseases. As an important category of phytochemicals, phenolic compounds universally exist in plants, and have been considered to have high antioxidant ability and free radical scavenging capacity, with the mechanism of inhibiting the enzymes responsible for ROS production and reducing highly oxidized ROS. Therefore, phenolic compounds have attracted increasing attention as potential agents for preventing and treating many oxidative stress-related diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases, cancer, ageing, diabetes mellitus and neurodegenerative diseases. This review summarizes current knowledge of natural polyphenols, including resource, bioactivities, bioavailability and potential toxicity.
Figures
References
-
- Arts I.C., Hollman P.C. Polyphenols and disease risk in epidemiologic studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005;81:317–325. - PubMed
-
- Kondratyuk T.P., Pezzuto J.M.J.P. Natural product polyphenols of relevance to human health. Pharm. Biol. 2004;42:46–63. doi: 10.3109/13880200490893519. - DOI
-
- Spencer J.P., Abd E.M.M., Minihane A.M., Mathers J.C. Biomarkers of the intake of dietary polyphenols: Strengths, limitations and application in nutrition research. Br. J. Nutr. 2008;99:12–22. - PubMed
-
- Kuhnau J. The flavonoids. A class of semi-essential food components: Their role in human nutrition. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 1976;24:91–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials