Nanoscale distribution of presynaptic Ca(2+) channels and its impact on vesicular release during development
- PMID: 25533484
- PMCID: PMC4305191
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.11.019
Nanoscale distribution of presynaptic Ca(2+) channels and its impact on vesicular release during development
Abstract
Synaptic efficacy and precision are influenced by the coupling of voltage-gated Ca(2+) channels (VGCCs) to vesicles. But because the topography of VGCCs and their proximity to vesicles is unknown, a quantitative understanding of the determinants of vesicular release at nanometer scale is lacking. To investigate this, we combined freeze-fracture replica immunogold labeling of Cav2.1 channels, local [Ca(2+)] imaging, and patch pipette perfusion of EGTA at the calyx of Held. Between postnatal day 7 and 21, VGCCs formed variable sized clusters and vesicular release became less sensitive to EGTA, whereas fixed Ca(2+) buffer properties remained constant. Experimentally constrained reaction-diffusion simulations suggest that Ca(2+) sensors for vesicular release are located at the perimeter of VGCC clusters (<30 nm) and predict that VGCC number per cluster determines vesicular release probability without altering release time course. This "perimeter release model" provides a unifying framework accounting for developmental changes in both synaptic efficacy and time course.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
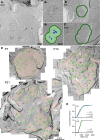

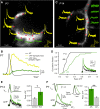
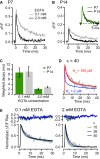




Comment in
-
On the brink: a new synaptic vesicle release model at the calyx of held.Neuron. 2015 Jan 7;85(1):6-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.12.038. Neuron. 2015. PMID: 25569343
References
-
- Bollmann J.H., Sakmann B. Control of synaptic strength and timing by the release-site Ca2+ signal. Nat. Neurosci. 2005;8:426–434. - PubMed
-
- Borst J.G., Sakmann B. Calcium influx and transmitter release in a fast CNS synapse. Nature. 1996;383:431–434. - PubMed
-
- Bucurenciu I., Kulik A., Schwaller B., Frotscher M., Jonas P. Nanodomain coupling between Ca2+ channels and Ca2+ sensors promotes fast and efficient transmitter release at a cortical GABAergic synapse. Neuron. 2008;57:536–545. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

