A heavy burden on young minds: the global burden of mental and substance use disorders in children and youth
- PMID: 25534496
- PMCID: PMC5922255
- DOI: 10.1017/S0033291714002888
A heavy burden on young minds: the global burden of mental and substance use disorders in children and youth
Abstract
Background: Mental and substance use disorders are common and often persistent, with many emerging in early life. Compared to adult mental and substance use disorders, the global burden attributable to these disorders in children and youth has received relatively little attention.
Method: Data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010 was used to investigate the burden of mental and substance disorders in children and youth aged 0-24 years. Burden was estimated in terms of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), derived from the sum of years lived with disability (YLDs) and years of life lost (YLLs).
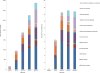
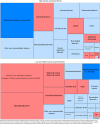
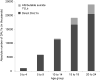
Results: Globally, mental and substance use disorders are the leading cause of disability in children and youth, accounting for a quarter of all YLDs (54.2 million). In terms of DALYs, they ranked 6th with 55.5 million DALYs (5.7%) and rose to 5th when mortality burden of suicide was reattributed. While mental and substance use disorders were the leading cause of DALYs in high-income countries (HICs), they ranked 7th in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) due to mortality attributable to infectious diseases.
Conclusions: Mental and substance use disorders are significant contributors to disease burden in children and youth across the globe. As reproductive health and the management of infectious diseases improves in LMICs, the proportion of disease burden in children and youth attributable to mental and substance use disorders will increase, necessitating a realignment of health services in these countries.
Keywords: mental and substance use disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. United States Medical Expenditure Panel Survey 2000–2009. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; Rockville, USA: 2009.
-
- APA. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV-TR) American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC: 2000.
-
- Apter A, Gtohelf D, Orbach I, Weizman R, Ratzoni G, Har-Even D, Sam T. Correlation of suicidal and violent behavior in different diagnostic categories in hospitalized adolescent patients. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 1995;34:912–918. - PubMed
-
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. Mental Health and Wellbeing: Profile of Adults, Australia 1997. Australian Bureau of Statistics; Canberra, Australia: 1997.
-
- Bardone AM, Moffitt TE, Caspi A, Dickson N, Silva PA. Adult mental health and social outcomes of adolescent girls with depression and conduct disorder. Development and Psychopathology. 1996;8:811–829.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

