A Bayesian framework for de novo mutation calling in parents-offspring trios
- PMID: 25535243
- PMCID: PMC4410659
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu839
A Bayesian framework for de novo mutation calling in parents-offspring trios
Abstract
Motivation: Spontaneous (de novo) mutations play an important role in the disease etiology of a range of complex diseases. Identifying de novo mutations (DNMs) in sporadic cases provides an effective strategy to find genes or genomic regions implicated in the genetics of disease. High-throughput next-generation sequencing enables genome- or exome-wide detection of DNMs by sequencing parents-proband trios. It is challenging to sift true mutations through massive amount of noise due to sequencing error and alignment artifacts. One of the critical limitations of existing methods is that for all genomic regions the same pre-specified mutation rate is assumed, which has a significant impact on the DNM calling accuracy.
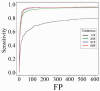
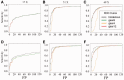
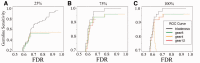
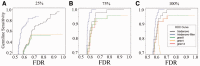
Results: In this study, we developed and implemented a novel Bayesian framework for DNM calling in trios (TrioDeNovo), which overcomes these limitations by disentangling prior mutation rates from evaluation of the likelihood of the data so that flexible priors can be adjusted post-hoc at different genomic sites. Through extensively simulations and application to real data we showed that this new method has improved sensitivity and specificity over existing methods, and provides a flexible framework to further improve the efficiency by incorporating proper priors. The accuracy is further improved using effective filtering based on sequence alignment characteristics.
Availability and implementation: The C++ source code implementing TrioDeNovo is freely available at https://medschool.vanderbilt.edu/cgg.
Contact: bingshan.li@vanderbilt.edu
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

