CESA TRAFFICKING INHIBITOR inhibits cellulose deposition and interferes with the trafficking of cellulose synthase complexes and their associated proteins KORRIGAN1 and POM2/CELLULOSE SYNTHASE INTERACTIVE PROTEIN1
- PMID: 25535279
- PMCID: PMC4326758
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.114.249003
CESA TRAFFICKING INHIBITOR inhibits cellulose deposition and interferes with the trafficking of cellulose synthase complexes and their associated proteins KORRIGAN1 and POM2/CELLULOSE SYNTHASE INTERACTIVE PROTEIN1
Abstract
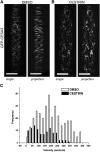
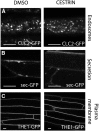
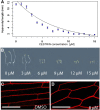
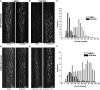
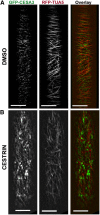
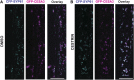
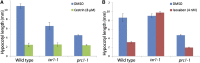
Cellulose synthase complexes (CSCs) at the plasma membrane (PM) are aligned with cortical microtubules (MTs) and direct the biosynthesis of cellulose. The mechanism of the interaction between CSCs and MTs, and the cellular determinants that control the delivery of CSCs at the PM, are not yet well understood. We identified a unique small molecule, CESA TRAFFICKING INHIBITOR (CESTRIN), which reduces cellulose content and alters the anisotropic growth of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) hypocotyls. We monitored the distribution and mobility of fluorescently labeled cellulose synthases (CESAs) in live Arabidopsis cells under chemical exposure to characterize their subcellular effects. CESTRIN reduces the velocity of PM CSCs and causes their accumulation in the cell cortex. The CSC-associated proteins KORRIGAN1 (KOR1) and POM2/CELLULOSE SYNTHASE INTERACTIVE PROTEIN1 (CSI1) were differentially affected by CESTRIN treatment, indicating different forms of association with the PM CSCs. KOR1 accumulated in bodies similar to CESA; however, POM2/CSI1 dissociated into the cytoplasm. In addition, MT stability was altered without direct inhibition of MT polymerization, suggesting a feedback mechanism caused by cellulose interference. The selectivity of CESTRIN was assessed using a variety of subcellular markers for which no morphological effect was observed. The association of CESAs with vesicles decorated by the trans-Golgi network-localized protein SYNTAXIN OF PLANTS61 (SYP61) was increased under CESTRIN treatment, implicating SYP61 compartments in CESA trafficking. The properties of CESTRIN compared with known CESA inhibitors afford unique avenues to study and understand the mechanism under which PM-associated CSCs are maintained and interact with MTs and to dissect their trafficking routes in etiolated hypocotyls.
© 2015 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cellulose synthase interactive protein 1 (CSI1) links microtubules and cellulose synthase complexes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jan 3;109(1):185-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1118560109. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22190487 Free PMC article.
-
KORRIGAN1 interacts specifically with integral components of the cellulose synthase machinery.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 10;9(11):e112387. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112387. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25383767 Free PMC article.
-
POM-POM2/cellulose synthase interacting1 is essential for the functional association of cellulose synthase and microtubules in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2012 Jan;24(1):163-77. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.093575. Epub 2012 Jan 31. Plant Cell. 2012. PMID: 22294619 Free PMC article.
-
Cellulose synthases and synthesis in Arabidopsis.Mol Plant. 2011 Mar;4(2):199-211. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssq079. Epub 2011 Feb 9. Mol Plant. 2011. PMID: 21307367 Review.
-
Making parallel lines meet: transferring information from microtubules to extracellular matrix.Cell Adh Migr. 2012 Sep-Oct;6(5):404-8. doi: 10.4161/cam.21121. Epub 2012 Aug 20. Cell Adh Migr. 2012. PMID: 22902763 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TNO1, a TGN-localized SNARE-interacting protein, modulates root skewing in Arabidopsis thaliana.BMC Plant Biol. 2017 Apr 11;17(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1024-4. BMC Plant Biol. 2017. PMID: 28399805 Free PMC article.
-
Actomyosin and CSI1/POM2 cooperate to deliver cellulose synthase from Golgi to cortical microtubules in Arabidopsis.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 17;14(1):7442. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43325-9. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37978293 Free PMC article.
-
A G protein-coupled receptor-like module regulates cellulose synthase secretion from the endomembrane system in Arabidopsis.Dev Cell. 2021 May 17;56(10):1484-1497.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2021.03.031. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Dev Cell. 2021. PMID: 33878345 Free PMC article.
-
The Regulation of Cellulose Biosynthesis in Plants.Plant Cell. 2019 Feb;31(2):282-296. doi: 10.1105/tpc.18.00760. Epub 2019 Jan 15. Plant Cell. 2019. PMID: 30647077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two Complementary Mechanisms Underpin Cell Wall Patterning during Xylem Vessel Development.Plant Cell. 2017 Oct;29(10):2433-2449. doi: 10.1105/tpc.17.00309. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Plant Cell. 2017. PMID: 28947492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atmodjo MA, Hao Z, Mohnen D (2013) Evolving views of pectin biosynthesis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64: 747–779 - PubMed
-
- Baskin TI. (2001) On the alignment of cellulose microfibrils by cortical microtubules: a review and a model. Protoplasma 215: 150–171 - PubMed
-
- Baskin TI. (2005) Anisotropic expansion of the plant cell wall. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21: 203–222 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

