Transdermal deferoxamine prevents pressure-induced diabetic ulcers
- PMID: 25535360
- PMCID: PMC4291638
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1413445112
Transdermal deferoxamine prevents pressure-induced diabetic ulcers
Abstract
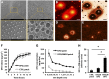
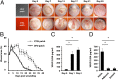
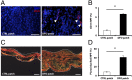
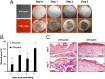
There is a high mortality in patients with diabetes and severe pressure ulcers. For example, chronic pressure sores of the heels often lead to limb loss in diabetic patients. A major factor underlying this is reduced neovascularization caused by impaired activity of the transcription factor hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α). In diabetes, HIF-1α function is compromised by a high glucose-induced and reactive oxygen species-mediated modification of its coactivator p300, leading to impaired HIF-1α transactivation. We examined whether local enhancement of HIF-1α activity would improve diabetic wound healing and minimize the severity of diabetic ulcers. To improve HIF-1α activity we designed a transdermal drug delivery system (TDDS) containing the FDA-approved small molecule deferoxamine (DFO), an iron chelator that increases HIF-1α transactivation in diabetes by preventing iron-catalyzed reactive oxygen stress. Applying this TDDS to a pressure-induced ulcer model in diabetic mice, we found that transdermal delivery of DFO significantly improved wound healing. Unexpectedly, prophylactic application of this transdermal delivery system also prevented diabetic ulcer formation. DFO-treated wounds demonstrated increased collagen density, improved neovascularization, and reduction of free radical formation, leading to decreased cell death. These findings suggest that transdermal delivery of DFO provides a targeted means to both prevent ulcer formation and accelerate diabetic wound healing with the potential for rapid clinical translation.
Keywords: angiogenesis; diabetes; drug delivery; small molecule; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: G.C.G., J.R., E.N., and M.G.G. are listed on the following patent assigned to Stanford University: Topical and Transdermal Delivery of HIF-1 Modulators to Prevent and Treat Chronic Wounds (20100092546).
Figures

References
-
- Blonde L. Improving care for patients with type 2 diabetes: Applying management guidelines and algorithms, and a review of new evidence for incretin agents and lifestyle intervention. Am J Manag Care. 2011;17(Suppl 14):S368–S376. - PubMed
-
- Golden SH. Emerging therapeutic approaches for the management of diabetes mellitus and macrovascular complications. Am J Cardiol. 2011;108(3) Suppl:59B–67B. - PubMed
-
- Jan YK, Shen S, Foreman RD, Ennis WJ. Skin blood flow response to locally applied mechanical and thermal stresses in the diabetic foot. Microvasc Res. 2013;89:40–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

