Fear and C-reactive protein cosynergize annual pulse increases in healthy adults
- PMID: 25535364
- PMCID: PMC4321278
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1418264112
Fear and C-reactive protein cosynergize annual pulse increases in healthy adults
Abstract
Recent international terror outbreaks notably involve long-term mental health risks to the exposed population, but whether physical health risks are also anticipated has remained unknown. Here, we report fear of terror-induced annual increases in resting heart rate (pulse), a notable risk factor of all-cause mortality. Partial least squares analysis based on 325 measured parameters successfully predicted annual pulse increases, inverse to the expected age-related pulse decline, in approximately 4.1% of a cohort of 17,380 apparently healthy active Israeli adults. Nonbiased hierarchical regression analysis among 27 of those parameters identified pertinent fear of terror combined with the inflammatory biomarker C-reactive protein as prominent coregulators of the observed annual pulse increases. In comparison, basal pulse primarily depended on general physiological parameters and reduced cholinergic control over anxiety and inflammation, together indicating that consistent exposure to terror threats ignites fear-induced exacerbation of preexisting neuro-immune risks of all-cause mortality.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; acetylcholinesterase; cholinergic status; pulse; terror.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
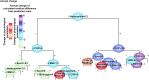
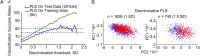
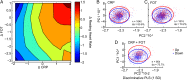
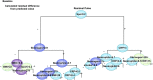

Comment in
-
Fear of terror and inflammation ignite heart health decline.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Feb 3;112(5):1248-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1424405112. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25617361 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Whalley MG, Brewin CR. Mental health following terrorist attacks. Br J Psychiatry. 2007;190:94–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

