HDAC inhibition imparts beneficial transgenerational effects in Huntington's disease mice via altered DNA and histone methylation
- PMID: 25535382
- PMCID: PMC4291662
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1415195112
HDAC inhibition imparts beneficial transgenerational effects in Huntington's disease mice via altered DNA and histone methylation
Abstract
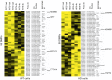
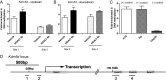
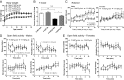
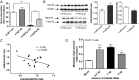
Increasing evidence has demonstrated that epigenetic factors can profoundly influence gene expression and, in turn, influence resistance or susceptibility to disease. Epigenetic drugs, such as histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors, are finding their way into clinical practice, although their exact mechanisms of action are unclear. To identify mechanisms associated with HDAC inhibition, we performed microarray analysis on brain and muscle samples treated with the HDAC1/3-targeting inhibitor, HDACi 4b. Pathways analyses of microarray datasets implicate DNA methylation as significantly associated with HDAC inhibition. Further assessment of DNA methylation changes elicited by HDACi 4b in human fibroblasts from normal controls and patients with Huntington's disease (HD) using the Infinium HumanMethylation450 BeadChip revealed a limited, but overlapping, subset of methylated CpG sites that were altered by HDAC inhibition in both normal and HD cells. Among the altered loci of Y chromosome-linked genes, KDM5D, which encodes Lys (K)-specific demethylase 5D, showed increased methylation at several CpG sites in both normal and HD cells, as well as in DNA isolated from sperm from drug-treated male mice. Further, we demonstrate that first filial generation (F1) offspring from drug-treated male HD transgenic mice show significantly improved HD disease phenotypes compared with F1 offspring from vehicle-treated male HD transgenic mice, in association with increased Kdm5d expression, and decreased histone H3 Lys4 (K4) (H3K4) methylation in the CNS of male offspring. Additionally, we show that overexpression of Kdm5d in mutant HD striatal cells significantly improves metabolic deficits. These findings indicate that HDAC inhibitors can elicit transgenerational effects, via cross-talk between different epigenetic mechanisms, to have an impact on disease phenotypes in a beneficial manner.
Keywords: epigenetic; histone; neurodegenerative; therapeutic; transgenerational.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors targeting HDAC3 and HDAC1 ameliorate polyglutamine-elicited phenotypes in model systems of Huntington's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2012 May;46(2):351-61. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.01.016. Neurobiol Dis. 2012. PMID: 22590724 Free PMC article.
-
The HDAC inhibitor 4b ameliorates the disease phenotype and transcriptional abnormalities in Huntington's disease transgenic mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Oct 7;105(40):15564-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804249105. Epub 2008 Sep 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18829438 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms Involved in Huntington's Disease Pathogenesis.J Huntingtons Dis. 2015;4(1):1-15. doi: 10.3233/JHD-159001. J Huntingtons Dis. 2015. PMID: 25813218 Review.
-
Selective histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition imparts beneficial effects in Huntington's disease mice: implications for the ubiquitin-proteasomal and autophagy systems.Hum Mol Genet. 2012 Dec 15;21(24):5280-93. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds379. Epub 2012 Sep 10. Hum Mol Genet. 2012. PMID: 22965876 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics of Huntington's Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;978:277-299. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-53889-1_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28523552 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of SETDB1 activity by APQ ameliorates heterochromatin condensation, motor function, and neuropathology in a Huntington's disease mouse model.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021 Dec;36(1):856-868. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2021.1900160. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33771089 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin accessibility and transcription dynamics during in vitro astrocyte differentiation of Huntington's Disease Monkey pluripotent stem cells.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2019 Nov 13;12(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s13072-019-0313-6. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2019. PMID: 31722751 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors - emerging roles in neuronal memory, learning, synaptic plasticity and neural regeneration.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016;14(1):55-71. doi: 10.2174/1570159x13666151021111609. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26487502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone Deacetylase Inhibition Enhances the Antitumor Activity of a MEK Inhibitor in Lung Cancer Cells Harboring RAS Mutations.Mol Cancer Ther. 2018 Jan;17(1):17-25. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0146. Epub 2017 Oct 27. Mol Cancer Ther. 2018. PMID: 29079711 Free PMC article.
-
Advances of HDAC inhibitors in tumor therapy: potential applications through immune modulation.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 27;15:1576781. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1576781. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40657246 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Deutsch SI, Rosse RB, Mastropaolo J, Long KD, Gaskins BL. Epigenetic therapeutic strategies for the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders: Ready for prime time? Clin Neuropharmacol. 2008;31(2):104–119. - PubMed
-
- Kazantsev AG, Thompson LM. Therapeutic application of histone deacetylase inhibitors for central nervous system disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7(10):854–868. - PubMed
-
- Cantley MD, Haynes DR. Epigenetic regulation of inflammation: Progressing from broad acting histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors to targeting specific HDACs. Inflammopharmacology. 2013;21(4):301–307. - PubMed
-
- Grayson DR, Kundakovic M, Sharma RP. Is there a future for histone deacetylase inhibitors in the pharmacotherapy of psychiatric disorders? Mol Pharmacol. 2010;77(2):126–135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

