The association between histone 3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) and prostate cancer: relationship with clinicopathological parameters
- PMID: 25535400
- PMCID: PMC4364597
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-994
The association between histone 3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) and prostate cancer: relationship with clinicopathological parameters
Abstract
Background: It is well established that genetic and epigenetic alterations are common events in prostate cancer, which may lead to aberrant expression of critical genes. The importance of epigenetic mechanisms in prostate cancer carcinogenesis is increasingly evident. In this study, the focus will be on histone modifications and the primary objectives are to map H3K27me3 marks and quantify RAR beta 2, ER alpha, SRC3, RGMA, PGR, and EZH2 gene expressions in prostate cancer tissues compared to normal tissues. In addition, a data analysis was made in connection with the clinicopathological parameters.
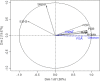
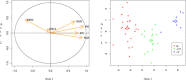
Methods: 71 normal specimens and 66 cancer prostate tissues were randomly selected in order to assess the proportion of the repressive H3K27me3 mark and gene expression. H3K27me3 level was evaluated by ChIP-qPCR and mRNA expression using RT-qPCR between prostate cancer and normal tissues. Subsequently, western-blotting was performed for protein detection. The analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed, and Tukey's test was used to correct for multiple comparisons (p-value threshold of 0.05). The principal component analysis (PCA) and discriminant factorial analysis (DFA) were used to explore the association between H3K27me3 level and clinicopathological parameters.
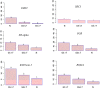
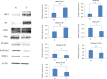
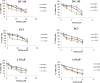
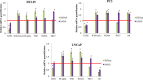
Results: The study demonstrated that H3K27me3 level was significantly enriched at the RAR beta 2, ER alpha, PGR, and RGMA promoter regions in prostate cancer tissues compared to normal tissues. After stratification by clinicopathological parameters, the H3K27me3 level was positively correlated with Gleason score, PSA levels and clinical stages for RAR beta 2, ER alpha, PGR, and RGMA. High H3K27me3 mark was significantly associated with decreased RAR beta 2, ER alpha, PGR and RGMA gene expressions in prostate cancer sample compared to the normal one. Moreover, the results showed that mRNA level of EZH2, AR and SRC3 are upregulated in prostate cancer compared to normal prostate tissues and this correlates positively with Gleason score, PSA levels and clinical stages. Obviously, these observations were confirmed by protein level using western-blot.
Conclusions: This data clearly demonstrated that H3K27me3 level correlated with aggressive tumor features. Also this study revealed that reverse correlation of RAR beta 2, ER alpha, PGR, and RGMA expressions with EZH2, SRC3, and AR expressions in prostate cancer tissues suggests that these genes are the target of EZH2. Therefore, all therapeutic strategies leading to histone demethylation with epigenetic drugs such as histone methyltransferase inhibitor may be relevant treatments against prostate cancer.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Histone trimethylation of the p53 gene by expression of a constitutively active prolactin receptor in prostate cancer cells.Chin J Physiol. 2013 Oct 31;56(5):282-90. doi: 10.4077/CJP.2013.BAB139. Epub 2013 Aug 31. Chin J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24032713
-
EZH2 dependent H3K27me3 is involved in epigenetic silencing of ID4 in prostate cancer.Oncotarget. 2014 Aug 30;5(16):7172-82. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2262. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25115397 Free PMC article.
-
Global analysis of H3K27me3 as an epigenetic marker in prostate cancer progression.BMC Cancer. 2017 Apr 12;17(1):261. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3256-y. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28403887 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations and deletions of PRC2 in prostate cancer.Bioessays. 2016 May;38(5):446-54. doi: 10.1002/bies.201500162. Epub 2016 Mar 22. Bioessays. 2016. PMID: 27000413 Review.
-
EZH2, an epigenetic driver of prostate cancer.Protein Cell. 2013 May;4(5):331-41. doi: 10.1007/s13238-013-2093-2. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Protein Cell. 2013. PMID: 23636686 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A new metabolic gene signature in prostate cancer regulated by JMJD3 and EZH2.Oncotarget. 2018 May 4;9(34):23413-23425. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25182. eCollection 2018 May 4. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29805743 Free PMC article.
-
The triterpenoid corosolic acid blocks transformation and epigenetically reactivates Nrf2 in TRAMP-C1 prostate cells.Mol Carcinog. 2018 Apr;57(4):512-521. doi: 10.1002/mc.22776. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Mol Carcinog. 2018. PMID: 29247555 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Identification of H3K9me2/H3K79me3 as an Epigenetic Barrier to Carcinogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 29;24(15):12158. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512158. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569534 Free PMC article.
-
The role of histone modifications and telomere alterations in the pathogenesis of diffuse gliomas in adults and children.J Neurooncol. 2017 Mar;132(1):1-11. doi: 10.1007/s11060-016-2349-9. Epub 2017 Jan 7. J Neurooncol. 2017. PMID: 28064387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SKP2 loss destabilizes EZH2 by promoting TRAF6-mediated ubiquitination to suppress prostate cancer.Oncogene. 2017 Mar;36(10):1364-1373. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.300. Epub 2016 Nov 21. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 27869166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rabiau N, Trraf H-K, Adjakly M, Bosviel R, Guy L, Fontana L, Bignon Y-J, Bernard-Gallon DJ. miRNAs differentially expressed in prostate cancer cell lines after soy treatment. In Vivo. 2011;25:917–921. - PubMed
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2407/14/994/prepub
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

