Protective effect of Korean Red Ginseng against glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 25535476
- PMCID: PMC4268568
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2014.06.001
Protective effect of Korean Red Ginseng against glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
Background: Glucocorticoids (GCs) are commonly used in many chemotherapeutic protocols and play an important role in the normal regulation of bone remodeling. However, the prolonged use of GCs results in osteoporosis, which is partially due to apoptosis of osteoblasts and osteocytes. In this study, effects of Korean Red Ginseng (KRG) on GC-treated murine osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells and a GC-induced osteoporosis mouse model were investigated.
Methods: MC3T3-E1 cells were exposed to dexamethasone (Dex) with or without KRG and cell viability was measured by the 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. Real-time polymerase chain reaction was performed to evaluate the apoptotic gene expression; osteogenic gene expression and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity were also measured. Western blotting was performed to evaluate the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) proteins. A GC-induced osteoporosis animal model was used for in vivo study.
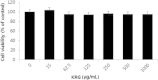
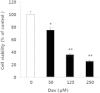
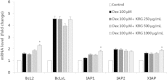
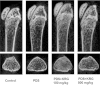
Results and conclusion: The MTT assay revealed that Korean Red Ginseng (KRG) prevents loss of cell viability caused by Dex-induced apoptosis in MC3T3E1 cells. Real-time polymerase chain reaction data showed that groups treated with both Dex and KRG exhibited lower mRNA levels of caspase-3 and -9, whereas the mRNA levels of Bcl2, IAPs, and XIAP increased. Moreover, groups treated with both Dex and KRG demonstrated increased mRNA levels of ALP, RUNX2, and bone morphogenic proteins as well as increased ALP activity in MC3T3-E1 cells, compared to cells treated with Dex only. In addition, KRG increased protein kinase B (AKT) phosphorylation and decreased c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) phosphorylation. Moreover, microcomputed tomography analysis of the femurs showed that GC implantation caused trabecular bone loss. However, a significant reduction of bone loss was observed in the KRG-treated group. These results suggest that the molecular mechanism of KRG in the GC-induced apoptosis may lead to the development of therapeutic strategies to prevent and/or delay osteoporosis.
Keywords: Korean Red Ginseng; Panax ginseng; dexamethasone; osteoblast; osteoporosis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Gastrodin protects MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts from dexamethasone-induced cellular dysfunction and promotes bone formation via induction of the NRF2 signaling pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Apr;41(4):2059-2069. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3414. Epub 2018 Jan 23. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29393365 Free PMC article.
-
Panax ginseng aqueous extract prevents pneumococcal sepsis in vivo by potentiating cell survival and diminishing inflammation.Phytomedicine. 2015 Oct 15;22(11):1055-61. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2015.07.005. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Phytomedicine. 2015. PMID: 26407948
-
4-Phenyl butyric acid prevents glucocorticoid-induced osteoblast apoptosis by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress.J Bone Miner Metab. 2017 Jul;35(4):366-374. doi: 10.1007/s00774-016-0778-3. Epub 2016 Sep 27. J Bone Miner Metab. 2017. PMID: 27678165
-
Ginseng, the natural effectual antiviral: Protective effects of Korean Red Ginseng against viral infection.J Ginseng Res. 2016 Oct;40(4):309-314. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2015.09.002. Epub 2015 Sep 16. J Ginseng Res. 2016. PMID: 27746682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The antioxidant activities of Korean Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng) and ginsenosides: A systemic review through in vivo and clinical trials.J Ginseng Res. 2021 Jan;45(1):41-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2020.09.006. Epub 2020 Oct 10. J Ginseng Res. 2021. PMID: 33437155 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An analysis of the combination frequencies of constituent medicinal herbs in prescriptions for the treatment of bone and joint disorder in Korean medicine: determination of a group of candidate prescriptions for universal use.Integr Med Res. 2017 Dec;6(4):344-353. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2017.09.001. Epub 2017 Sep 19. Integr Med Res. 2017. PMID: 29296561 Free PMC article.
-
Bone remodeling effects of Korean Red Ginseng extracts for dental implant applications.J Ginseng Res. 2020 Nov;44(6):823-832. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2020.05.003. Epub 2020 May 27. J Ginseng Res. 2020. PMID: 33192126 Free PMC article.
-
Antiosteoporosis and bone protective effect of dieckol against glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in rats.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 19;13:932488. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.932488. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36060953 Free PMC article.
-
The osteogenesis-promoting effects of alpha-lipoic acid against glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis through the NOX4, NF-kappaB, JNK and PI3K/AKT pathways.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 13;7(1):3331. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03187-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28611356 Free PMC article.
-
Korean red ginseng extract prevents bone loss in an oral model of glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis in mice.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 12;15:1268134. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1268134. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38533264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Advani S., LaFrancis D., Bogdanovic E., Taxel P., Raisz L.G., Kream B.E. Dexamethasone suppresses in vivo levels of bone collagen synthesis in neonatal mice. Bone. 1997;20:41–46. - PubMed
-
- Canalis E., Delany A.M. Mechanisms of glucocorticoid action in bone. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;966:73–81. - PubMed
-
- Zalavras C., Shah S., Birnbaum M.J., Frenkel B. Role of apoptosis in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis and osteonecrosis. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2003;13:221–235. - PubMed
-
- Gohel A., McCarthy M.B., Gronowicz G. Estrogen prevents glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in osteoblasts in vivo and in vitro. Endocrinology. 1999;140:5339–5347. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

