Assessment of the effects of ketamine-fentanyl combination versus propofol-remifentanil combination for sedation during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
- PMID: 25535501
- PMCID: PMC4268195
Assessment of the effects of ketamine-fentanyl combination versus propofol-remifentanil combination for sedation during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
Abstract
Background: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) as a diagnostic and treatment procedure is used in most biliary tract and pancreatic. Either sedation or general anesthesia could be considered for this procedure. Combining a sedative with an opioid agent can provide effective moderate sedation. This study compared the impact of ketamine-fentanyl (KF) versus propofol-remifentanil (PR) on sedation scale in patients undergoing ERCP.
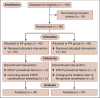
Materials and methods: As a double-blinded randomized clinical trial, 80 patients selected by convenient sampling, allocated randomly into two groups. KF group received ketamine 0.5 mg/kg body weight intravenously over 60 s and then fentanyl 1 mcg/kg body weight intravenously. PR group received propofol l mg/kg body weight intravenously over 60 s and then remifentanil 0.05 mcg/kg body weight/min intravenously. Intravenous (IV) infusion of propofol was maintained by 50 mcg/kg body weight/min throughout ERCP. Ramsay Sedation Score, vital signs, oxygen saturation (SpO2), recovery score (modified Aldrete score) and visual analog scales of pain intensity, and endoscopist's satisfaction were considered as measured outcomes. All analysis were analyzed by SPSS Statistics version 22 and using t-test, Chi-square and repeated measured ANOVA and Mann-Whitney tests for data analysis.
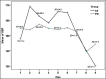
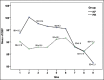
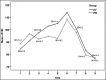
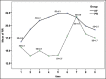
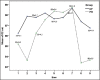
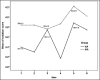
Results: Respiratory rate and SpO2 level during the time intervals were lower in PR group (P < 0.001). Sedation score at intervals was not significantly different (P = 0.07). The frequency of apnea in PR group was significantly higher than the KF group (P = 0.003). The percentage of need to supplemental oxygen in PR group was 35.1% that was also significantly higher than 8.8% in the KF group (P = 0.008), but the dosage frequency was significantly higher in KF group (P < 0.001). The KF and PR groups average length of stay in the recovery room were 50.71 standard deviation (SD = 9.99) and 42.57 (SD = 11.99) minutes, respectively, indicating a significant difference (P = 0.003). The mean severity of nausea in KF and PR groups was, respectively, 2.74 confidence interval (CI = 1.68-3.81) and 0.43 (CI = 0.11-0.75), that was significantly higher in KF group (P < 0.001). The average score of surgeon satisfaction in both KF and PR groups were 7.69 (CI = 7.16-8.21) and 8.65 (CI = 8.25-9.05), respectively, which was higher in KF group (P = 0.004), but the average level of patients satisfaction in KF group was 8.86 (CI = 8.53-9.19) and in PR group was 8.95 (CI - 8.54-9.35) that were not significantly different (P = 0.074).
Conclusion: There is no statistically significant difference between KF and PR combinations in sedation score, but PR combination provides better pain control, with less nausea and shorter recovery time while causing more respiratory side effects, that is, apnea and need to oxygen.
Keywords: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; fentanyl; ketamine; propofol; remifentanil.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Thomson A, Andrew G, Jones DB. Optimal sedation for gastrointestinal endoscopy: Review and recommendations. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25:469–78. - PubMed
-
- Chowdhury IH, Maruf AA, Lateef KA, Reza SM, Hye MA. Sedation for ERCP-comparison between ketamine diazepam combination with propofol fntanyl combination. J Bangladesh Soc Anaesthesiol. 2009;20:45–50.
-
- Mazzon D, Germanà B, Poole D, Celato M, Bernardi L, Calleri G, et al. Conscious sedation during endoscopic retrograde colangiopancreatography: Implementation of SIED-SIAARTI-ANOTE guidelines in Belluno Hospital. Minerva Anestesiol. 2005;71:101–9. - PubMed
-
- American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Sedation and Analgesia by Non-Anesthesiologists. Practice guidelines for sedation and analgesia by non-anesthesiologists. Anesthesiology. 2002;96:1004–17. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
