Displacements of fiducial markers in patients with prostate cancer treated with image guided radiotherapy: A single-institution descriptive study
- PMID: 25535583
- PMCID: PMC4268593
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rpor.2014.08.002
Displacements of fiducial markers in patients with prostate cancer treated with image guided radiotherapy: A single-institution descriptive study
Abstract
Aim: To describe daily displacements when using fiducial markers as surrogates for the target volume in patients with prostate cancer treated with IGRT.
Background: The higher grade of conformity achieved with the use of modern radiation technologies in prostate cancer can increase the risk of geographical miss; therefore, an associated protocol of IGRT is recommended.
Materials and methods: A single-institution, retrospective, consecutive study was designed. 128 prostate cancer patients treated with daily on-line IGRT based on 2D kV orthogonal images were included. Daily displacement of the fiducial markers was considered as the difference between the position of the patient when using skin tattoos and the position after being relocated using fiducial markers. Measures of central tendency and dispersion were used to describe fiducial displacements.
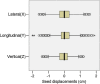
Results: The implant itself took a mean time of 15 min. We did not detect any complications derived from the implant. 4296 sets of orthogonal images were identified, 128 sets of images corresponding to treatment initiation were excluded; 91 (2.1%) sets of images were excluded from the analysis after having identified that these images contained extreme outlier values. If IGRT had not been performed 25%, 10% or 5% of the treatments would have had displacements superior to 4, 7 or 9 mm respectively in any axis.
Conclusions: Image guidance is required when using highly conformal techniques; otherwise, at least 10% of daily treatments could have significant displacements. IGRT based on fiducial markers, with 2D kV orthogonal images is a convenient and fast method for performing image guidance.
Keywords: Developing countries; Fiducial markers; IGRT; IMRT; Prostate cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J., Shin H.R., Bray F., Forman D., Mathers C., Parkin D.M. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2010. GLOBOCAN 2008, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 10 [Internet] Available in: http://globocan.iarc.fr [cited 17.05.11]
-
- Mendenhall W.M., Nichols R.C., Henderson R., Mendenhall N.P. Is radical prostatectomy the “gold standard” for localized prostate cancer? Am J Clin Oncol. 2010;33(October (5)):511–515. - PubMed
-
- Button M.R., Staffurth J.N. Clinical application of image-guided radiotherapy in bladder and prostate cancer. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 2010;22(October (8)):698–706. - PubMed
-
- Staffurth J. Radiotherapy Development Board. A review of the clinical evidence for intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 2010;22(October (8)):643–657. - PubMed
-
- Yoon M., Kim D., Shin D.H. Inter- and intrafractional movement-induced dose reduction of prostate target volume in proton beam treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;71(July (4)):1091–1102. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources