Gender differences in the association of sleep apnea and inflammation
- PMID: 25535861
- PMCID: PMC4468024
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.11.013
Gender differences in the association of sleep apnea and inflammation
Abstract
Over the last 15years, many studies have established an association of sleep apnea with inflammation and metabolic aberrations. However, no controlled studies have examined potential gender effects in this association. We recruited 120 middle-aged, predominantly non-obese mild-to-moderate sleep apneics and controls (62 males, 58 females). All participants underwent a clinical history, physical examination, and 1-night 8-h polysomnography recording and provided a single fasting blood sample for assessment of interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1), C-reactive protein (CRP), leptin, and adiponectin levels. Among non-sleep apneics, females had higher levels of TNFR1 (p=0.01), CRP (p=0.005), leptin (p<0.001), and adiponectin (p<0.001) compared to males, independent of age and body mass index. When analyzed separately by gender, sleep apneic men had elevated TNFR1 (p=0.04), CRP (p=0.06) and IL-6 (p=0.11) relative to control men; in sleep apneic females, only CRP was elevated (p=0.04). Furthermore, CRP was associated with apnea severity in a dose-response manner (p-linear=0.04 in both genders) and was independently associated with comorbid hypertension in apnea (p-linear=0.005 for women; p-linear=0.09 for men). In conclusion, although women have naturally higher levels of inflammatory and metabolic markers than men, sleep apneic men appear to have a more severe inflammatory profile compared to women. Our findings suggest that these markers should be analyzed and interpreted separately in men and women, and that a single measure of plasma CRP appears to be a clinically-useful marker of apnea severity and comorbid cardiovascular morbidity.
Keywords: Apnea; CRP; Gender; Hypertension; Inflammation; Sleep.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
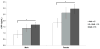
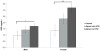
References
-
- Akira S, Hirano T, Taga T, Kishimoto T. Biology of multifunctional cytokines: IL 6 and related molecules (IL 1 and TNF) FASEB J. 1990;4:2860–7. - PubMed
-
- Bixler EO, Vgontzas AN, Lin HM, Ten Have T, Leiby BE, Vela-Bueno A, Kales A. Association of hypertension and sleep-disordered breathing. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160:2289–95. - PubMed
-
- Bixler EO, Vgontzas AN, Lin HM, Ten Have T, Rein J, Vela-Bueno A, Kales A. Prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in women: effects of gender. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:608–13. - PubMed
-
- Bixler EO, Vgontzas AN, Ten Have T, Tyson K, Kales A. Effects of age on sleep apnea in men: I. Prevalence and severity. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157:144–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

