Enhancement of cellular radiation sensitivity through degradation of Chk1 by the XIAP-XAF1 complex
- PMID: 25535897
- PMCID: PMC4623052
- DOI: 10.4161/15384047.2014.962305
Enhancement of cellular radiation sensitivity through degradation of Chk1 by the XIAP-XAF1 complex
Abstract
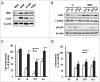
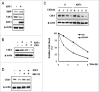
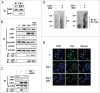
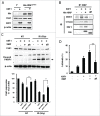
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) and Chk1 are potential molecular targets in radiotherapy. However, their molecular association in the regulation of radiation sensitivity has been rarely studied. Here, we show that XIAP modulates radiation sensitivity by regulating stability of Chk1 in lung cancer cells. Both Chk1 and XIAP are highly expressed in various lung cancer cells. Overexpression of XIAP increased cell survival following genotoxic treatments by preventing downregulation of Chk1. However, XIAP reversed Chk1-protective activity in the presence of XIAP-associated factor 1 (XAF1) by degrading Chk1 via ubiquitination-dependent proteasomal proteolysis. The XIAP-XAF1 complex-mediated Chk1 degradation also required CUL4A and DDB1. Chk1 or XIAP was associated with DDB1 and CUL4A. Depletion of CUL4A or DDB1 prevented the XIAP-XAF1-mediated Chk1 degradation suggesting involvement of a CUL4A/DDB1-based E3 ubiquitin ligase in the process or its collaboration with XIAP E3 ligase activity. Taken together, our findings show that XIAP plays a dual role in modulation of Chk1 stability and cell viability following IR. In the absence of XAF1, XIAP stabilizes Chk1 under IR with corresponding increase of cell viability. By contrast, when XAF1 is overexpressed, XIAP facilitates Chk1 degradation, which leads to enhancement of radiation sensitivity. This selective regulation of Chk1 stability by XIAP and XAF1 could be harnessed to devise a strategy to modulate radiation sensitivity in lung cancer cells.
Keywords: Chk1; Chk1, Checkpoint kinase 1; DDR, DNA damage responses; DNA damage response; IFN-γ, interferon-gamma; IR, ionizing radiation; RING domain; XAF1; XAF1, XIAP-associated factor 1; XIAP; XIAP, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis; radiation sensitivity; synthetic lethality.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Degradation of survivin by the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP)-XAF1 complex.J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 7;282(36):26202-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M700776200. Epub 2007 Jul 5. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17613533
-
Interferon-gamma enhances radiation-induced cell death via downregulation of Chk1.Cancer Biol Ther. 2012 Sep;13(11):1018-25. doi: 10.4161/cbt.20990. Epub 2012 Jul 24. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22825336 Free PMC article.
-
Domain organization of XAF1 and the identification and characterization of XIAP(RING) -binding domain of XAF1.Protein Sci. 2012 Oct;21(10):1418-28. doi: 10.1002/pro.2126. Epub 2012 Sep 17. Protein Sci. 2012. PMID: 22811387 Free PMC article.
-
DDB1 targets Chk1 to the Cul4 E3 ligase complex in normal cycling cells and in cells experiencing replication stress.Cancer Res. 2009 Mar 15;69(6):2630-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3382. Epub 2009 Mar 10. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19276361 Free PMC article.
-
XIAP as a ubiquitin ligase in cellular signaling.Cell Death Differ. 2010 Jan;17(1):54-60. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2009.81. Cell Death Differ. 2010. PMID: 19590513 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IAP-Mediated Protein Ubiquitination in Regulating Cell Signaling.Cells. 2020 Apr 30;9(5):1118. doi: 10.3390/cells9051118. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32365919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ANTP-SMACN7 fusion peptide alone induced high linear energy transfer irradiation radiosensitization in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines.Cancer Biol Med. 2021 Sep 21;19(7):983-94. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0569. Cancer Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34546667 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Amidine Derivative K1586 Sensitizes Colorectal Cancer Cells to Ionizing Radiation by Inducing Chk1 Instability.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 16;25(8):4396. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084396. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673980 Free PMC article.
-
A novel Chk1-binding peptide that enhances genotoxic sensitivity through the cellular redistribution of nuclear Chk1.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Nov;38(5):1490-1498. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2762. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 28025997 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant splicing and drug resistance in AML.J Hematol Oncol. 2016 Sep 10;9(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s13045-016-0315-9. J Hematol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27613060 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sancar A, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Unsal-Kaçmaz K, Linn S. Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the DNA damage checkpoints. Annu Rev Biochem 2004; 73:39-85; PMID; http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.011303.073723 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhao H, Watkins JL, Piwnica-Worms H. Disruption of the checkpoint kinase 1/cell division cycle 25A pathway abrogates ionizing radiation-induced S and G2 checkpoints. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99(23):14795-800; PMID; http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.182557299 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sørensen CS, Syljuåsen RG, Falck J, Schroeder T, Rönnstrand L, Khanna KK, Zhou BB, Bartek J, Lukas J. Chk1 regulates the S phase checkpoint by coupling the physiological turnover and ionizing radiation-induced accelerated proteolysis of Cdc25A. Cancer Cell 2003; 3(3):247-58; PMID; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1535-6108(03)00048-5 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Falck J, Mailand N, Syljuåsen RG, Bartek J, Lukas J. The ATM-Chk2-Cdc25A checkpoint pathway guards against radioresistant DNA synthesis. Nature 2001; 410(6830):842-7; PMID; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35071124 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD, Rich JN. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 2006;444(7120):756-60; PMID; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature05236 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
