Pyoluteorin derivatives induce Mcl-1 degradation and apoptosis in hematological cancer cells
- PMID: 25535900
- PMCID: PMC4623387
- DOI: 10.4161/15384047.2014.972799
Pyoluteorin derivatives induce Mcl-1 degradation and apoptosis in hematological cancer cells
Abstract
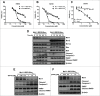
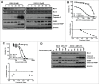
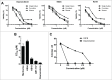
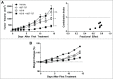
Mcl-1, a pro-survival member of the Bcl-2 protein family, is an attractive target for cancer therapy. We have recently identified the natural product marinopyrrole A (maritoclax) as a novel small molecule Mcl-1 inhibitor. Here, we describe the structure-activity relationship study of pyoluteorin derivatives based on maritoclax. To date, we synthesized over 30 derivatives of maritoclax and evaluated their inhibitory actions and cytotoxicity toward Mcl-1-dependent cell lines. As a result, several functional groups were identified in the pyoluteorin motif that significantly potentiate biological activity. A number of such derivatives, KS04 and KS18, interacted with Mcl-1 in a conserved fashion according to NMR spectroscopy and molecular modeling. KS04 and KS18 induced apoptosis selectively in Mcl-1-dependent but not Bcl-2-dependent K562 cells through selective Mcl-1 down-regulation, and synergistically enhanced apoptosis in combination with ABT-737. Moreover, the intraperitoneal administration of KS18 (10 mg/kg/d) and ABT-737 (20 mg/kg/d) significantly suppressed the growth of ABT-737-resistant HL-60 xenografts in nude mice without apparent toxicity. Overall, we identified the pharmacophore of pyoluteorin derivatives that act as potent and promising Mcl-1 antagonists against Mcl-1-dependent hematological cancers.
Keywords: ABTR, ABT-737 resistant; AML, Acute Myeloid Leukemia; AUCinf, area under curve extrapolated to time infinity; AUClast, area under curve until last observed timepoint; Apoptosis; BH3, Bcl-2 homology domain 3; Bcl-2 family; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma-2; CHX, Cycloheximide; CL, rate of plasma clearance; Cmax, maximal plasma concentration; EC50, Half maximal effective concentration; IRES, Internal ribosome entry site; LD50, median lethal dose; MTD, Maximal tolerated dose; Mcl-1; Mcl-1, Myeloid cell leukemia-1; NMR, Nuclear magnetic resonance; PARP, Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase; SAR, Structure-activity relationship; T1/2, plasma half-life; Tmax, time to maximal plasma concentration; VD, Volume of distribution; i.p., Intraperitoneal; leukemia; lymphoma; maritoclax; multiple myeloma; pyoluteorin.
Figures

References
-
- Liu Q, Wang HG. Anti-cancer drug discovery and development: Bcl-2 family small molecule inhibitors. Commun Integr Biol 2012; 5:557-65; PMID:23336025; http://dx.doi.org/10.4161/cib.21554 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA: Cancer J Clin 2014; 64:9-29; PMID:24399786 - PubMed
-
- Tsujimoto Y, Finger LR, Yunis J, Nowell PC, Croce CM. Cloning of the chromosome breakpoint of neoplastic B cells with the t(14;18) chromosome translocation. Science 1984; 226:1097-9; PMID:6093263; http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.6093263 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schena M, Larsson LG, Gottardi D, Gaidano G, Carlsson M, Nilsson K, Caligaris-Cappio F. Growth- and differentiation-associated expression of bcl-2 in B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood 1992; 79:2981-9; PMID:1375120 - PubMed
-
- Harada N, Hata H, Yoshida M, Soniki T, Nagasaki A, Kuribayashi N, Kimura T, Matsuzaki H, Mitsuya H. Expression of Bcl-2 family of proteins in fresh myeloma cells. Leukemia: Off J Leukemia Soc Am, Leukemia Res Fund, UK 1998; 12:1817-20; PMID:9823959; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401168 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
