Alteco endotoxin hemoadsorption in Gram-negative septic shock patients
- PMID: 25538412
- PMCID: PMC4271277
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-5229.146305
Alteco endotoxin hemoadsorption in Gram-negative septic shock patients
Abstract
Background and aims: Severe sepsis and septic shock are common causes of mortality and morbidity in an intensive care unit setting. Endotoxin, derived from the outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria, is considered a major factor in the pathogenesis of sepsis. This study investigated the effect of Alteco endotoxin hemoadsorption device on Gram-negative septic shock patients.
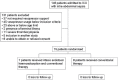
Materials and methods: An open, controlled, prospective, randomized, single-center trial was conducted between February 2010 and June 2012. Patients with septic shock due to intra-abdominal sepsis were randomized to either conventional therapy (n = 8) or conventional therapy plus two 2-hourly sessions of Alteco endotoxin hemoadsorption (n = 7). Primary endpoint was the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score changes from 0 to 72 h. Secondary end points included vasopressor requirement, PaO2/FiO2 ratio (PFR), length of stay (LOS), and 28-day mortality.
Results: This study was terminated early as interim analysis showed a low probability of significant findings. No significant difference was noted between the two groups with respect to change in SOFA score, vasopressor score, PFR, LOS, and 28-day mortality. Side-effect was minimal.
Conclusions: We could not identify any clinical benefit on the addition of Alteco endotoxin hemoadsorption to conventional therapy in patients who suffered from intra-abdominal sepsis with shock. The side effect profile of this novel device was acceptable.
Keywords: Endotoxins; hemoadsorption; outcome; septic shock.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Casey LC, Balk RA, Bone RC. Plasma cytokine and endotoxin levels correlate with survival in patients with the sepsis syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1993;119:771–8. - PubMed
-
- Alexander C, Rietschel ET. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides and innate immunity. J Endotoxin Res. 2001;7:167–202. - PubMed
-
- Beutler B, Poltorak A. Positional cloning of Lps, and the general role of toll-like receptors in the innate immune response. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2000;11:143–52. - PubMed
-
- Marshall JC, Foster D, Vincent JL, Cook DJ, Cohen J, Dellinger RP, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic implications of endotoxemia in critical illness: Results of the MEDIC study. J Infect Dis. 2004;190:527–34. - PubMed
-
- Greenman RL, Schein RM, Martin MA, Wenzel RP, MacIntyre NR, Emmanuel G, et al. A controlled clinical trial of E5 murine monoclonal IgM antibody to endotoxin in the treatment of gram-negative sepsis. The XOMA Sepsis Study Group. JAMA. 1991;266:1097–102. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources