A diagnosis of haemolytic-uraemic syndrome blurred by alcohol abuse
- PMID: 25540209
- PMCID: PMC4281547
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2014-205940
A diagnosis of haemolytic-uraemic syndrome blurred by alcohol abuse
Abstract
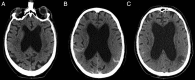
A 60-year-old man with a history of alcohol abuse was admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) for status epilepticus. At first, laboratory and imagery findings were almost normal, and the symptoms were attributed to severe alcohol withdrawal due to a history of gastroenteritis reported by his family. But, during the following days, haemolytic anaemia, thrombocytopenia, acute renal failure, and ischaemic and haemorrhagic lesions seen on a cerebral CT scan led to the diagnosis of haemolytic-uraemic syndrome (HUS). Despite these severe complications, the patient made a good recovery following ICU and plasma exchange with fresh frozen plasma (FFP), but cognitive deficit still existed after 1 month. It is important to know that neurological manifestations can precede typical biological and radiological signs in HUS, and to not be misled in the diagnosis process, especially when a more common differential diagnosis is possible.
2014 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Haemolytic uraemic syndrome - a rare case report of bloody diarrhoea in adults.BMC Gastroenterol. 2019 Aug 28;19(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12876-019-1071-4. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31462210 Free PMC article.
-
Haemolytic uraemic syndrome following acute pancreatitis.JOP. 2005 Jul 8;6(4):365-8. JOP. 2005. PMID: 16006689
-
Unusual manifestation of diarrhea-associated haemolytic uraemic syndrome in an adult.Ren Fail. 2008;30(3):331-4. doi: 10.1080/08860220701861102. Ren Fail. 2008. PMID: 18350454
-
Haemolytic uraemic syndrome.Paediatrician. 1979;8(5-6):378-93. Paediatrician. 1979. PMID: 392409 Review.
-
Haemolytic uraemic syndrome.J Intern Med. 2017 Feb;281(2):123-148. doi: 10.1111/joim.12546. Epub 2016 Oct 10. J Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 27723152 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
