Decomposition of surface EMG signals from cyclic dynamic contractions
- PMID: 25540220
- PMCID: PMC4359986
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00555.2014
Decomposition of surface EMG signals from cyclic dynamic contractions
Abstract
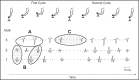
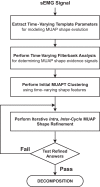
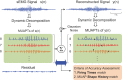
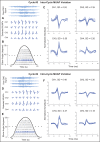
Over the past 3 decades, various algorithms used to decompose the electromyographic (EMG) signal into its constituent motor unit action potentials (MUAPs) have been reported. All are limited to decomposing EMG signals from isometric contraction. In this report, we describe a successful approach to decomposing the surface EMG (sEMG) signal collected from cyclic (repeated concentric and eccentric) dynamic contractions during flexion/extension of the elbow and during gait. The increased signal complexity introduced by the changing shapes of the MUAPs due to relative movement of the electrodes and the lengthening/shortening of muscle fibers was managed by an incremental approach to enhancing our established algorithm for decomposing sEMG signals obtained from isometric contractions. We used machine-learning algorithms and time-varying MUAP shape discrimination to decompose the sEMG signal from an increasingly challenging sequence of pseudostatic and dynamic contractions. The accuracy of the decomposition results was assessed by two verification methods that have been independently evaluated. The firing instances of the motor units had an accuracy of ∼90% with a MUAP train yield as high as 25. Preliminary observations from the performance of motor units during cyclic contractions indicate that during repetitive dynamic contractions, the control of motor units is governed by the same rules as those evidenced during isometric contractions. Modifications in the control properties of motoneuron firings reported by previous studies were not confirmed. Instead, our data demonstrate that the common drive and hierarchical recruitment of motor units are preserved during concentric and eccentric contractions.
Keywords: dynamic contractions; firing rate; gait; motor units.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures



References
-
- Bertram MF, Nishida T, Minieka MM, Janssen I, Levy CE. Effects of temperature on motor unit action potentials during isometric contraction. Muscle Nerve 18: 1443–1446, 1995. - PubMed
-
- De Luca CJ. Myoelectrical manifestations of localized muscular fatigue in humans. Crit Rev Biomed Eng 11: 251–279, 1984. - PubMed
-
- De Luca CJ, Adam A, Wotiz R, Gilmore LD, Nawab SH. Decomposition of surface EMG signals. J Neurophysiol 96: 1646–1657, 2006. - PubMed
-
- De Luca CJ, Erim Z. Common drive of motor units in regulation of muscle force. Trends Neurosci 17: 299–305, 1994. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

