Multi-facets of Corticotropin-releasing Factor in Modulating Inflammation and Angiogenesis
- PMID: 25540945
- PMCID: PMC4288099
- DOI: 10.5056/jnm14076
Multi-facets of Corticotropin-releasing Factor in Modulating Inflammation and Angiogenesis
Abstract
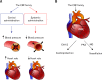
The family of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) composed of 4 ligands including CRF, urocortin (Ucn) 1, Ucn2, and Ucn3 is expressed both in the central nervous system and the periphery including the gastrointestinal tract. Two different forms of G protein coupled receptors, CRF1 and CRF2, differentially recognize CRF family members, mediating various biological functions. A large body of evidence suggests that the CRF family plays an important role in regulating inflammation and angiogenesis. Of particular interest is a contrasting role of the CRF family during inflammatory processes. The CRF family can exert both proand anti-inflammatory functions depending on the type of receptors, the tissues, and the disease phases. In addition, there has been a growing interest in a possible role of the CRF family in angiogenesis. Regulation of angiogenesis by the CRF family has been shown to modulate endogenous blood vessel formation, inflammatory neovascularization and cardiovascular function. This review outlines the effect of the CRF family and its receptors on 2 major biological events: inflammation and angiogenesis, and provides a possibility of their application for the treatment of inflammatory vascular diseases.
Keywords: Angiogenesis effect; Corticotropin-releasing factor; Inflammation; Urocortins.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

