MicroRNA-302a functions as a putative tumor suppressor in colon cancer by targeting Akt
- PMID: 25542007
- PMCID: PMC4277419
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115980
MicroRNA-302a functions as a putative tumor suppressor in colon cancer by targeting Akt
Retraction in
-
Retraction: MicroRNA-302a Functions as a Putative Tumor Suppressor in Colon Cancer by Targeting Akt.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 25;10(9):e0139497. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139497. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26407228 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
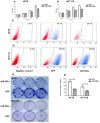
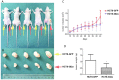
Micro RNAs (miRNAs) are important regulators involved in various physical and pathological processes, including cancer. The miRNA-302 family has been documented as playing a critical role in carcinogenesis. In this study, we investigated the role of miRNA-302a in colon cancer. MiRNA-302a expression was detected in 44 colon cancer tissues and 10 normal colon tissues, and their clinicopathological significance was analyzed. Cell proliferation and cell cycle analysis were performed on colon cancer cells that stably expressed miRNA-302a. The target gene of miRNA-302a and the downstream pathway were further investigated. Compared with normal colon tissues, miRNA-302a expression was downregulated in colon cancer tissues. Overexpression of miRNA-302a induced G1/S cell cycle arrest in colon cancer cells, and suppressed colon cancer cell proliferation both in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, miRNA-302a inhibited AKT expression by directly binding to its 3' untranslated region, resulting in subsequent alterations of the AKT-GSK3β-cyclin D1 pathway. These results reveal miRNA-302a as a tumor suppressor in colon cancer, suggesting that miRNA-302a may be used as a potential target for therapeutic intervention in colon cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2013) Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Fidler IJ (1990) Critical factors in the biology of human cancer metastasis: 28th G. H. A. Clowes Memorial Award Lecture. Cancer Res 50:6130–6138. - PubMed
-
- Chang GJ, Kaiser AM, Mills S, Rafferty JF, Buie WD (2012) Practice parameters for the management of colon cancer. Dis Colon Rectum 55:831–843. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

