Piloting laboratory quality system management in six health facilities in Nigeria
- PMID: 25542022
- PMCID: PMC4277469
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116185
Piloting laboratory quality system management in six health facilities in Nigeria
Abstract
Background: Achieving accreditation in laboratories is a challenge in Nigeria like in most African countries. Nigeria adopted the World Health Organization Regional Office for Africa Stepwise Laboratory (Quality) Improvement Process Towards Accreditation (WHO/AFRO- SLIPTA) in 2010. We report on FHI360 effort and progress in piloting WHO-AFRO recognition and accreditation preparedness in six health facility laboratories in five different states of Nigeria.
Method: Laboratory assessments were conducted at baseline, follow up and exit using the WHO/AFRO- SLIPTA checklist. From the total percentage score obtained, the quality status of laboratories were classified using a zero to five star rating, based on the WHO/AFRO quality improvement stepwise approach. Major interventions include advocacy, capacity building, mentorship and quality improvement projects.
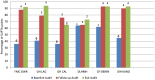
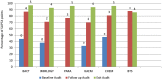
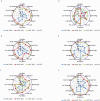
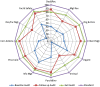
Results: At baseline audit, two of the laboratories attained 1- star while the remaining four were at 0- star. At follow up audit one lab was at 1- star, two at 3-star and three at 4-star. At exit audit, four labs were at 4- star, one at 3-star and one at 2-star rating. One laboratory dropped a 'star' at exit audit, while others consistently improved. The two weakest elements at baseline; internal audit (4%) and occurrence/incidence management (15%) improved significantly, with an exit score of 76% and 81% respectively. The elements facility and safety was the major strength across board throughout the audit exercise.
Conclusion: This effort resulted in measurable and positive impact on the laboratories. We recommend further improvement towards a formal international accreditation status and scale up of WHO/AFRO- SLIPTA implementation in Nigeria.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of mentorship on WHO-AFRO Strengthening Laboratory Quality Improvement Process Towards Accreditation (SLIPTA).Afr J Lab Med. 2012 Feb 16;1(1):6. doi: 10.4102/ajlm.v1i1.6. eCollection 2012. Afr J Lab Med. 2012. PMID: 29062726 Free PMC article.
-
Innovative strategies for a successful SLMTA country programme: The Rwanda story.Afr J Lab Med. 2014 Nov 3;3(2):217. doi: 10.4102/ajlm.v3i2.217. eCollection 2014. Afr J Lab Med. 2014. PMID: 29043189 Free PMC article.
-
Critical review of the Stepwise Laboratory Improvement Process Towards Accreditation (SLIPTA): suggestions for harmonization, implementation and improvement.Trop Med Int Health. 2012 Mar;17(3):361-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2011.02917.x. Epub 2011 Nov 18. Trop Med Int Health. 2012. PMID: 22093245
-
Strengthening national health laboratories in sub-Saharan Africa: a decade of remarkable progress.Trop Med Int Health. 2014 Apr;19(4):450-8. doi: 10.1111/tmi.12269. Epub 2014 Feb 10. Trop Med Int Health. 2014. PMID: 24506521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strengthening Laboratory Management Toward Accreditation, A Model Program for Pathology Laboratory Improvement.Clin Lab Med. 2018 Mar;38(1):131-140. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2017.10.010. Epub 2017 Dec 19. Clin Lab Med. 2018. PMID: 29412877 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic applications for Lassa fever in limited-resource settings.BMJ Glob Health. 2019 Feb 7;4(Suppl 2):e001119. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2018-001119. eCollection 2019. BMJ Glob Health. 2019. PMID: 30899576 Free PMC article.
-
H3Africa partnerships to empower clinical research sites to generate high-quality biological samples.Afr J Lab Med. 2020 Mar 18;9(1):935. doi: 10.4102/ajlm.v9i1.935. eCollection 2020. Afr J Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 32284923 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating laboratory request forms submitted to haematology and blood transfusion departments at a hospital in Northwest Nigeria.Afr J Lab Med. 2016 May 12;5(1):381. doi: 10.4102/ajlm.v5i1.381. eCollection 2016. Afr J Lab Med. 2016. PMID: 28879111 Free PMC article.
-
Quality Management Systems implementation in public medical laboratories; A sustainable approach to health system strengthening in Lagos State, Nigeria.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 2;20(6):e0319409. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319409. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40455874 Free PMC article.
-
Investments for effective functionality of health systems towards Universal Health Coverage in Africa: A scoping review.PLOS Glob Public Health. 2022 Sep 23;2(9):e0001076. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0001076. eCollection 2022. PLOS Glob Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36962623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abimiku AG (2009) Building laboratory infrastructure to support scale-up of HIV/AIDS treatment, care, and prevention: in-country experience. Am J Clin Pathol 131:875–886 Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dop... - PubMed
-
- Audu RA, Sylvester-Ikondu U, Onwuamah CK, Salu OB, Ige F a, et al. (2011) Experience of quality management system in a clinical laboratory in Nigeria. Afr J Lab Med 1:1–5 Available: http://www.ajlmonline.org/index.php/ajlm/article/view/18. Accessed 6 September 2013 - PMC - PubMed
-
- International Organisation for Standardisation (2012) ISO 15189: 2012: Medical laboratories Requirements for quality and competence. Geneva Int Organ Stand http://www.iso.org. Available: http://www.iso.org.
-
- Rabinovitch A (2002) The college of American Pathologists laboratory accreditation program. Accredit Qual Assur 7:473–476 10.1007/s00769-002-0537-0 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

