An estrogen-responsive module in the ventromedial hypothalamus selectively drives sex-specific activity in females
- PMID: 25543145
- PMCID: PMC4324838
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.12.011
An estrogen-responsive module in the ventromedial hypothalamus selectively drives sex-specific activity in females
Abstract
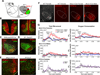
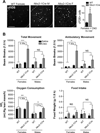
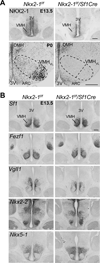
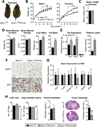
Estrogen-receptor alpha (ERα) neurons in the ventrolateral region of the ventromedial hypothalamus (VMHVL) control an array of sex-specific responses to maximize reproductive success. In females, these VMHVL neurons are believed to coordinate metabolism and reproduction. However, it remains unknown whether specific neuronal populations control distinct components of this physiological repertoire. Here, we identify a subset of ERα VMHVL neurons that promotes hormone-dependent female locomotion. Activating Nkx2-1-expressing VMHVL neurons via pharmacogenetics elicits a female-specific burst of spontaneous movement, which requires ERα and Tac1 signaling. Disrupting the development of Nkx2-1(+) VMHVL neurons results in female-specific obesity, inactivity, and loss of VMHVL neurons coexpressing ERα and Tac1. Unexpectedly, two responses controlled by ERα(+) neurons, fertility and brown adipose tissue thermogenesis, are unaffected. We conclude that a dedicated subset of VMHVL neurons marked by ERα, NKX2-1, and Tac1 regulates estrogen-dependent fluctuations in physical activity and constitutes one of several neuroendocrine modules that drive sex-specific responses.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
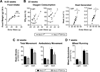
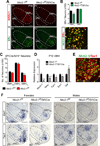

References
-
- Brailoiu E, Dun SL, Brailoiu GC, Mizuo K, Sklar LA, Oprea TI, Prossnitz ER, Dun NJ. Distribution and characterization of estrogen receptor G protein-coupled receptor 30 in the rat central nervous system. J Endocrinol. 2007;193:311–321. - PubMed
-
- Brobeck JR, Wheatland M, Strominger JL. Variations in regulation of energy exchange associated with estrus, diestrus and pseudopregnancy in rats. Endocrinology. 1947;40:65–72. - PubMed
-
- Carr MC. The emergence of the metabolic syndrome with menopause. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:2404–2411. - PubMed
-
- Cheung CC, Kurrasch DM, Liang JK, Ingraham HA. Genetic labeling of steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1) neurons in mice reveals ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMH) circuitry beginning at neurogenesis and development of a separate non-SF-1 neuronal cluster in the ventrolateral VMH. J Comp Neurol. 2012;521:1268–1288. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Coppola G. Designing, performing, and interpreting a microarray-based gene expression study. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;793:417–439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- P30 DK026743/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK099722/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS062691/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK099722/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08DK076721/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH081880/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK063592/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK80427/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063720/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK080427/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK098320/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01DK098320/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK076721/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK063592/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH049428/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

